Artificial intelligence is reshaping how people write, analyze, and design through prompts. What started as trial-and-error phrasing has grown into a structured craft that blends context, precision, and safety. As models advance, the real task is building reliable systems around them: governed, consistent, and practical enough for teams to trust.
The evolution of the prompt engineering process has dramatically advanced from a stand-alone prompt to multi-modal, to a comprehensive system management framework and to safe. When multi-modal and agentic models develop, the transition will happen naturally. The goals of designing better models and implementing tighter governance, however, remain the same. It is the constant evaluation of the outputs and continual iteration and evaluation of the system itself that need to be commonplace by 2026 (not the exception).
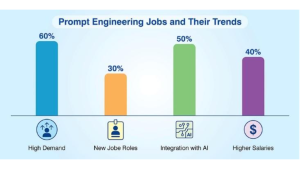
As there is growing demand for effective prompt engineering, trends indicate that new kind of jobs are likely to be filled in the next two years.
Top 10 AI Prompt Engineering Trends
It is an effort to showcase examples of real-life manifestations of each trend and the steps your organization can take to leverage prompt engineering trends. Prompt engineering service provider companies create prompt engineering-based systems that work and are scalable and accountable. Most humans over-engineer their stack and waste a large part of their lives trying to create perfect prompts.
Let’s get into what’s new and how to make it work.
1) Mega-prompts as “prompt contracts”
At some point, almost every team will try to construct a mega-prompt, which will do everything you need. The results are amazing and if it works, the output is consistent, with homogenous results and a good tone and structure.
But there is a downside. The greater the revision of the prompt, the more it slows down, the more costly and weaker it is. A large prompt slows things down, takes more tokens and showcases erratic behaviour due to shoddy input context. Everyone who has wasted valuable time in trying to repair their prompts to make them usable again, understands this frustration.
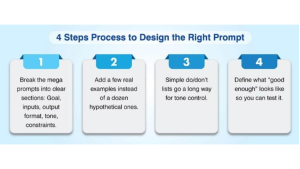
How to design it right
A lighter approach helps.
Tie-ins that make it work at scale
For bigger teams, a bit of structure and restraint pays off:
- Prompt version control keeps changes traceable.
- Reusable fragments save time when similar prompts share tone or layout.
- Rollback options help when a new version drifts off course.
By making small and modular units of instructions, one can control the prompts with much ease and render scaling it to higher purposes. The prompts become more refined once these units grow.
2) Adaptive and intelligent prompts
Static prompts are no longer desirable today. The modern system is adapted internally as it carries on its processes of information: takes the material context as needed, excludes the useless elements and gradually adapts itself.
Instead of starting from scratch every time, adaptive prompts use the last existing context that includes previous conversations, results of various tools used, and user preferences and/or source of information already included in the circle of knowledge.
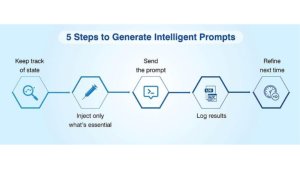
Follow the loop
Most setups follow a simple loop:
Real-time checks
By retaining the old context, the system can give the proper results and prevent crowding the model. The system operates on the same principle of action and need of thought as a human being. It uses the existing context to solve problems every time.
3) Multimodal Prompt Engineering (text + image + audio + UI)
Structure and placement
A prompt comprising text, images, audio, or UI state has some ordering aspects that must be considered.
An image should be inserted early in the prompt so that the model grasps first that desired visual information.
If diagrams or screenshots comprise regions of interest a more specific reference should be made to the area such as “top right quadrant of graph” or “row 3 column B”.
Identifiers should be employed clearly as to what is taken out (extraction goals) as well as formats (output schema) given for the response required e.g. a JSON format with fields for the issue, severity, evidence URL etc.
The same type of examples can work on a verbal (namely audio) basis (a request is, “mark the turns of the speakers with timestamps”) or UI basis (an example would be “pull out the selected rows in the grid and state the filter property”).
Reasoning and output
Keep the chain of thought that the model carries out separate from the output so that the model may do its reasoning internally and still not display its methodology.
The output presented to the user should be that which is visible e.g. finished piece of information, short analysis or coherent format type of result.
This aids the low latency and non-crowded display result.
Emerging direction
One early but exciting frontier is augmented reality prompt integration. Imagine technicians scanning a circuit board to get guided overlays or warehouse staff pointing a camera at a shelf to trigger pick lists. It’s a glimpse of prompt engineering trends moving beyond screens into real-world contexts.
A very early but new exciting modelling frontier is going to be augmented reality prompt integration. Imagine technicians using the scans of a circuit board to get overlay-guided systems or warehouse staff locating the camera on the shelf to actively create pick lists.
This is the first hint that systems based on prompts going to grow beyond computer systems into reality.
4) Automated / Self-Refining Prompts
Automated prompting adheres to repeatable loop: draft → self-critique → revise prompt or plan → re-run.
The model will look over its own output and revise the instructions given to it and re-run through until the response results are homogeneous. This is a kind of built-in copy editor which improves the output quality quietly over every iteration.
Where it helps
This format is useful for long form reports, code updates, data cleaning, analytical storytelling where built-in iteration is an implicit advantage. All with a bit of guardrails to manage it.
Guardrails for control
Handled this way, self-refining prompts evolve quietly in the background, giving you steadier output and fewer manual fixes.
5) Governance, Ethics, and Bias-Aware Prompting
Ethical and governance-aware prompting ensures AI systems remain fair, transparent, and accountable. It embeds fairness into design, separates contexts, and continuously monitors performance to mitigate bias and uphold responsible AI practices.
Fairness by design
Fairness inherent in governance starts at the prompt level.
Build fairness goals into the instructions in such a way that it finds out what fairness and balance would look like.
It is important to include examples of counterfactual alternate paradigms to test for bias and track reasons that led design choices being made. This would lead to changes in designs driving far more transparent measures than reactive ones.
Context separation
User context separate from system context. Have the model know your organization policy and the nature of input. Always check outside data or checks of validity to avoid misinformation or vulnerability in injections.
Ongoing monitoring
Track practical signals, hallucination rate, safety, latency, cost, and user satisfaction. Recognize ethical and bias-aware prompting solutions based on proven performance in governance logs, to track interventions that work.
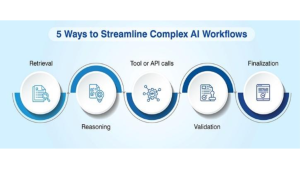
6) Prompt Orchestration Tools (Agents, Flows, Evaluations)
Prompt orchestration tools streamline complex AI workflows by connecting agents, flows, and evaluations. They enable structured, testable, and scalable prompt management, making experimentation traceable, reproducible, and ready for reliable deployment. This keeps complex operations structured and auditable.
Teams build flows that chains tasks like this:
This keeps complex operations structured and auditable.
Key features to look for
Modern orchestration tools need visual flow graphs, dataset-backed evaluations, and A/B testing for comparing variants. Add tracing to see where outputs drift, and CI/CD hooks to deploy safely. These features make experimentation repeatable rather than manual.
Why it matters
This will take prompts which are otherwise isolated sections of text. They gradually work the prompts into processes which are manageable, reproducible, testable and safe. Chip away at them, and get clearer transitions from one agent to another cutting down hidden logic and more debugging.
7) Prompt Version Control and Prompt IDEs
Prompt version control and IDEs bring software-level discipline to prompt development. They enable branching, testing, collaboration, and safe rollbacks, ensuring reproducibility, compliance, and seamless teamwork across evolving prompt workflows.
As prompts become more complex, then versioning is non-negotiable.
Use branches, diffs, pull requests, evaluations of tests, rollbacks, exactly as for software.
Small reviewable changes help teams on alignment
Everything is linked. Store prompts with datasets, and suites of evaluation. New versions are promoted if they pass the hurdles of safety and performance benchmarks. This guarantees reproducibility and compliance to experimental work.
Keep everything linked
Store prompts alongside their datasets and evaluation suites. Promote a version only when it clears performance and safety thresholds. This keeps experiments reproducible and compliant.
Why versioning is helpful
Database versions and IDEs offer collaboration and acceptance in prompt constructions.
It is possible to have teams distributed, testing, sharing and providing prompts efficiently and rapidly, without any worry about either where or what had changed or why.
8) No-Code AI Prompt Platforms for Business Teams
No-code AI prompt platforms democratize prompt creation, enabling business users to build and automate workflows through intuitive visual interfaces, while maintaining governance, security, and seamless integration with enterprise AI operations.
Building without code
Prompt creation is becoming accessible to a wider audience (business users) due to the availability of No Code platforms. Users can create and test workflows utilizing visual builders, templates, and connectors that do not require coding. Creating an orchestration workflow is very similar to utilizing drag-and-drop functionality to create a workflow.
One can get customer insights or ticket summaries promptly through this method.
Governance still matters
Ensure you establish and maintain access as defined by your role and approve processes. Telemetry and usage logging can ensure that the prompts used are both secure, consistent, and traceable.
Workflow automation link
When combined with automated workflows generated from prompts, no-code platforms provide a clear path for business operations to leverage AI capabilities and offer a “voice” to non-technical teams based on how prompts affect their daily work.
9) Domain-Specific Prompt Tuning and Task Libraries
Domain-specific prompt tuning and task libraries enable organizations to reuse validated prompts, enforce compliance, and achieve precision, reducing prompt drift, improving accuracy, and aligning AI outputs with organizational context and vocabulary.
Function-specific AI Prompt Libraries
As large organizations start to develop domain-specific task libraries for each department with compliance and tone guidelines, organizations can now develop fewer new prompts and instead use previously validated prompts.
Precision through structure
To prevent prompt drift and hallucination, use combination of a few shot exemplars with strict output schemas to deliver more precise results.
Providing your model with examples based on your own data, and then tying the examples to your data using strict formatting rules, will give your model the precision required to produce quality results. No need to develop yet another mega-prompt!
Outcome
General-purpose AI engines will generate much more specialized and trusted results after being trained using domain-specific AI prompts.
Organizations will significantly reduce the time required to onboard teams to use AI engines, reduce risk associated with those engines, and have those responses to match organization’s specific vocabulary and policies.
10) Skills and Team Practices for the Next Wave
The next wave of prompt engineering demands multidisciplinary teams with technical fluency, design critique skills, and adaptive collaboration models, where humans oversee governance while AI agents execute and optimize complex tasks efficiently.
Core technical fluency
In addition to knowledge of orchestration methodologies and best practices, knowledge of version control methodologies and best practices, and the ability to measure the effectiveness of prompts utilizing datasets, the minimum technical skills required of prompt developers/engineers today include:
Knowledge of how to build, test and deploy prompts in addition to wording prompts.
Design and critique mindset
Prompt developers/engineers should have knowledge of technical design and a critique mindset.
Multimodal prompt engineering process needs technical design skills. Developers/engineers should be able to write clear instructions. The primary focus of a prompt engineer is improving those prompts critiquing the flows effectively.
How teams will operate
A common expectation of future team operations will be a model where humans define their goals and constraints. While the reviewer reviews and approves the release and deployment of the AI agent, the AI agent completes the tasks efficiently.
This is a hybrid model where humans will continue to judge, while automating the repetitive tasks.
Conclusion
From “clever” one-off (prompt) solutions to fully developed (orchestrated) systems: prompt-engineered systems are being designed as context-dependent, multi-modal, auto-generated, and governed. Teams that adopt an orchestrated system of flow for their teams and standardized orchestration flows and use version-controlled prompts and bias/security guardrails will experience more accurate results, fewer risks and a shorter time to value.
This practical path is straightforward: Start with one end-to-end flow, add evaluation and threshold criteria, and then scale your library across various domains. The steady differentiators of evolving models will be clearly defined prompt contracts, adaptive contexts, and the discipline to govern, the foundation of reliable production AI.