In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, organizations are locked in a constant battle against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. As malicious actors continue to innovate, leveraging cutting-edge technologies becomes imperative.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming the way organizations detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats, emerging as game-changers in cybersecurity.
Advanced Threat Detection and Real-Time Response
One of the most significant advantages of AI and ML in cybersecurity is their ability to enhance threat detection capabilities. In the realm of cybersecurity, leveraging AI and ML technologies has emerged as a cornerstone for fortifying defense mechanisms. One of the most significant advantages of AI and ML in this domain is their ability to enhance threat detection capabilities, crucial insights found in any reputable cybersecurity guide.
Traditional security systems often struggle to keep pace with the sheer volume and complexity of modern cyber threats. However, AI-powered threat detection tools can identify a high percentage of cyber threats, a significant improvement compared to human analysts alone.
These advanced tools leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed. With the ability to process large volumes of malware samples rapidly, AI-driven threat detection enables real-time response, minimizing the window of vulnerability and preventing data breaches. Compliance with NERC CIP standards is also becoming increasingly crucial, particularly in the energy sector, where AI and ML can play a vital role in enhancing security posture and mitigating risks associated with critical infrastructure.
Moreover, AI-driven behavioral analytics play a crucial role in comprehending normal user behavior and detecting deviations that may indicate security breaches. Continuous monitoring of user activities enables these systems to detect insider threats with high accuracy, rendering them a critical component of modern cybersecurity strategies.
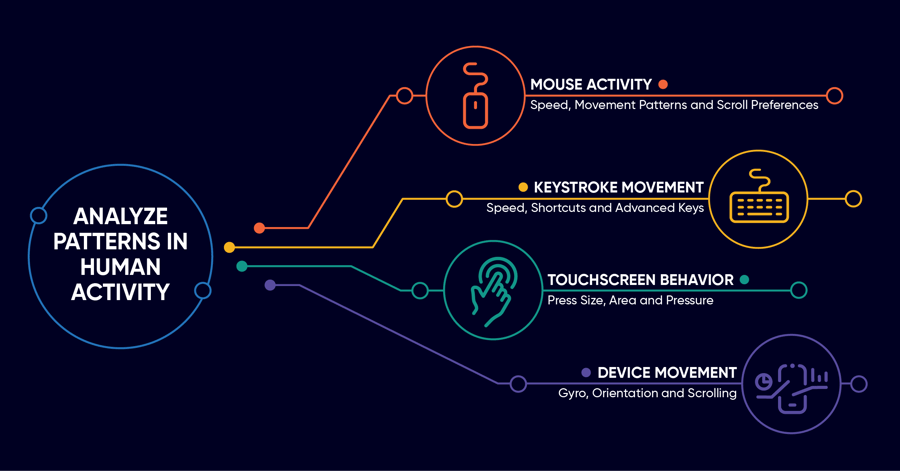
AI and ML are being leveraged across numerous cybersecurity domains, including but not limited to:
Proactive Security Posture and Zero-Trust Architecture
Moving from reactive to proactive, AI also plays a pivotal role in establishing a robust security posture. By anticipating threats, AI helps organizations stay a step ahead of cyber adversaries. AI-based predictive threat hunting can identify a significant proportion of threats before they cause any damage, allowing organizations to fortify their defenses and mitigate potential risks.
Additionally, integrating AI into zero-trust architectures significantly reduces the risk of data breaches. These advanced security models rely on continuous verification of users and devices, ensuring that access is granted only when necessary and revoked immediately upon detecting anomalous behavior.
AI-driven user authentication using behavioral biometrics boasts high accuracy rates, offering a robust and seamless solution for secure access management. By continuously monitoring user behavior patterns, such as keystroke dynamics and mouse movements, AI can detect potential impersonation attempts and prevent unauthorized access.
AI-Driven Automation in Incident Response
The benefits of AI extend beyond detection and prevention. Automation of incident response is another area where AI proves invaluable, optimizing operations and reducing manual workload. AI and machine learning can automate a significant proportion of cybersecurity tasks, drastically reducing the burden on human analysts.
Automated incident response powered by AI can cut down the mean time to resolve (MTTR) incidents, allowing for quicker mitigation and recovery from cyber attacks. By automating routine tasks such as threat triage, containment, and remediation, AI frees up valuable human resources to focus on more complex and strategic activities.
| Manual Incident Response | AI-Driven Automated Response |
| Slower response times | Near real-time response |
| Prone to human error | Consistent and accurate |
| Limited scalability | Highly scalable |
| Reactive approach | Proactive and predictive |
Leveraging AI for Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics powered by AI further enhance an organization’s ability to anticipate and prepare for potential threats, transforming raw data into actionable insights. AI predictive analytics can forecast cyber threats with reasonable accuracy, providing critical foresight into potential attack vectors.
Additionally, AI-driven vulnerability assessment tools can identify more vulnerabilities than traditional manual methods, ensuring comprehensive security evaluations. By continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities and weaknesses, organizations can proactively address potential entry points for cyber threats, reducing their overall risk exposure.
AI in Advanced Threat Intelligence
Beyond internal security measures, AI enhances threat intelligence by integrating and analyzing vast amounts of data from external sources, offering a broader perspective on emerging threats. AI-powered threat intelligence platforms can process large volumes of indicators of compromise (IoCs) rapidly, allowing for comprehensive threat assessments.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques enable these platforms to extract valuable insights from unstructured data sources, such as forums, blogs, and news articles, with high accuracy. By leveraging NLP, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the latest cyber threats, attack vectors, and potential countermeasures, enriching their overall threat intelligence.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers undeniable advantages in cybersecurity, it’s crucial to acknowledge the challenges and ethical considerations that accompany its use:
Challenges:
- Misuse of AI by Attackers: Malicious actors could potentially develop AI-powered attacks designed to bypass traditional security measures. These AI-driven attacks could be highly sophisticated and difficult to detect.
- Data Privacy Concerns: AI systems rely on vast amounts of data for training and operation. This raises concerns about data privacy, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Ensuring data anonymization and robust data governance practices are essential.
- Explainability and Transparency: Some AI models used in cybersecurity are complex and lack transparency. This “black box” nature makes it difficult to understand how AI arrives at its decisions, potentially leading to biased or unintended consequences.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI models can inherit biases from the data they are trained on. Biased data can lead to discriminatory outcomes, such as wrongly flagging certain user activities as malicious.
Ethical Considerations:
- Accountability: As AI plays a more prominent role in cybersecurity decisions, it’s crucial to establish clear lines of accountability. Who is responsible if an AI system makes a wrong decision that leads to a security breach?
- Human Oversight: While AI automates many tasks, human oversight remains essential. Security professionals should understand how AI systems work and be able to intervene when necessary.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: AI models require ongoing monitoring and improvement to ensure they remain effective and unbiased.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does AI improve threat detection in cybersecurity?
AI improves threat detection by analyzing vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that traditional methods might miss. This allows for faster and more accurate identification of potential threats.
2. How does AI automate incident response in cybersecurity?
AI can automate various tasks in incident response, such as threat triage, containment, and remediation. This reduces the workload on human analysts and significantly decreases the mean time to resolve (MTTR) incidents.
3. What is the role of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in AI-driven threat intelligence?
NLP techniques enable AI-powered threat intelligence platforms to extract valuable insights from unstructured data sources like forums, blogs, and news articles, enriching the overall threat intelligence gathered.
Conclusion
As we have seen, AI and machine learning are revolutionizing cybersecurity, offering unprecedented capabilities in threat detection, prevention, and response. By leveraging these advanced technologies, organizations can gain a significant advantage in the ongoing battle against cyber threats.
However, it is essential to address the accompanying challenges and ethical dilemmas to fully realize the potential of AI in cybersecurity. Responsible AI use, transparent decision-making processes, and robust governance frameworks are crucial for maintaining trust and accountability.
As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, embracing AI and machine learning will be pivotal for organizations seeking to stay ahead of cyber adversaries and protect their critical assets.