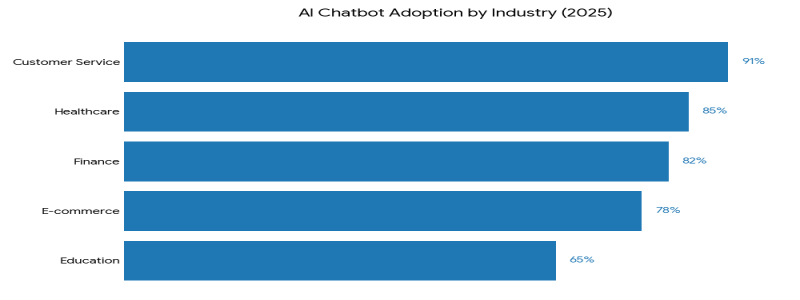
Artificial intelligence chatbots have evolved from simple rule-based systems into sophisticated conversational agents that are fundamentally reshaping how businesses interact with customers and how individuals access information. As we navigate through 2025, the AI chatbot landscape has matured significantly, driven by advances in natural language processing, machine learning, and the widespread adoption of large language models.
From Simple Scripts to Intelligent Conversations
The journey of chatbots began decades ago with primitive programs like ELIZA in the 1960s, which could only match patterns and provide pre-scripted responses. Today’s AI chatbots represent a quantum leap in capability. According to Grand View Research, the global chatbot market was valued at $5.13 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 23.3% from 2024 to 2030, reflecting the technology’s increasing sophistication and adoption.
Modern AI chatbots leverage transformer-based architectures and deep learning to understand context, maintain coherent conversations across multiple turns, and even exhibit a form of reasoning. They can interpret user intent, handle ambiguous queries, and provide responses that feel remarkably human-like.
The Technology Behind Modern AI Chatbots
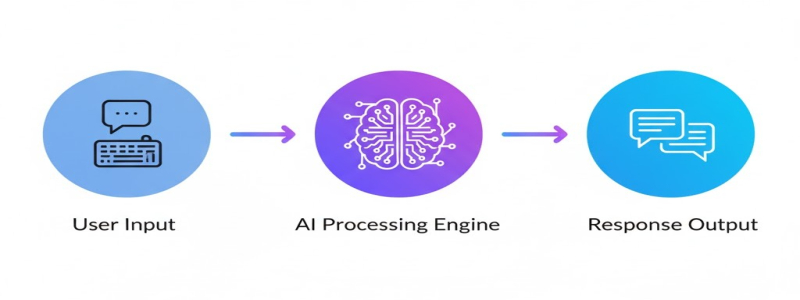
At the core of contemporary AI chatbots lies a complex stack of technologies working in harmony. Natural language processing (NLP) enables these systems to parse human language, identifying entities, sentiments, and intentions within user messages. Machine learning algorithms continuously improve chatbot performance by learning from interactions.
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has been particularly transformative. According to IBM’s research, RAG allows chatbots to access external knowledge bases in real-time, combining the generative capabilities of large language models with the accuracy of information retrieval systems. This hybrid approach significantly reduces hallucinations and ensures responses are grounded in factual, up-to-date information.
Vector databases and semantic search capabilities have further enhanced chatbot intelligence. These technologies enable chatbots to understand the meaning behind queries rather than relying solely on keyword matching.
Industry Applications Driving Adoption
The versatility of AI chatbots has led to widespread adoption across virtually every industry sector. In healthcare, chatbots are streamlining patient scheduling, providing preliminary symptom assessments, and offering mental health support. A study published in JAMA Network Open found that AI chatbots demonstrated empathetic and high-quality responses to patient questions, sometimes even surpassing physician responses in perceived quality.
The financial services sector has embraced chatbots for customer service, fraud detection alerts, and personalized financial advice. Banks and fintech companies report significant reductions in operational costs while simultaneously improving customer satisfaction scores. Juniper Research estimates that chatbots in banking will save financial institutions over $7.3 billion globally by 2023, a figure that continues to grow.
E-commerce platforms have integrated AI chatbots to provide product recommendations, answer customer inquiries, and guide users through purchasing decisions. These conversational commerce tools have proven particularly effective at reducing cart abandonment rates and increasing average order values by offering personalized shopping assistance at scale.
Enhancing Customer Experience and Operational Efficiency
One of the most compelling benefits of AI chatbots is their ability to provide 24/7 customer support without the limitations of human staff schedules. This round-the-clock availability meets the expectations of modern consumers who demand instant responses regardless of time zones or business hours. Salesforce research indicates that 64% of customers expect real-time assistance regardless of when they contact a company.
Beyond availability, AI chatbots excel at handling high volumes of simultaneous conversations. While a human agent might manage one or two conversations at a time, a well-designed chatbot system can engage with thousands of users concurrently. This scalability enables businesses to maintain service quality during peak periods without proportionally increasing staff.
The data collection and analysis capabilities of AI chatbots provide another strategic advantage. Every interaction generates valuable insights into customer preferences, pain points, and behavioral patterns. Businesses can analyze these conversation logs to identify trends, improve products and services, and refine their overall customer experience strategy.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementation
Despite their capabilities, AI chatbots face several challenges that organizations must address thoughtfully. Understanding context remains a persistent difficulty, particularly with complex, multi-layered queries or conversations requiring deep domain expertise. While large language models have improved contextual understanding, they can still misinterpret nuanced requests or struggle with highly specialized technical questions.
The phenomenon of AI hallucinations when chatbots generate confident-sounding but factually incorrect responses presents a significant risk, especially in high-stakes industries like healthcare, legal services, and finance. Organizations implementing chatbots must establish robust validation mechanisms and clear escalation paths to human experts when accuracy is critical. Research from Stanford University found that legal hallucinations in large language models are pervasive, highlighting the need for careful oversight.
Privacy and data security concerns cannot be overlooked. Chatbots handling sensitive customer information must comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, as well as industry-specific requirements, such as HIPAA in healthcare. Organizations need transparent data handling policies and secure infrastructure to protect user information and maintain trust. Understanding the risks and disadvantages of chatbots is essential for responsible implementation.
The Human-AI Collaboration Model
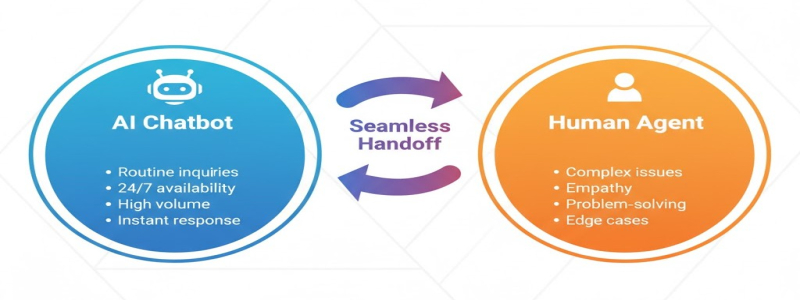
The most successful chatbot implementations recognize that AI should augment rather than replace human agents. The hybrid model, where chatbots handle routine inquiries and seamlessly transfer complex issues to human staff, combines the efficiency of automation with the empathy and problem-solving capabilities of people.
This collaboration extends beyond simple handoffs. AI chatbots can assist human agents by suggesting responses, surfacing relevant information from knowledge bases, and summarizing previous interactions. This support enables human agents to work more efficiently and provide higher-quality service. According to McKinsey research, AI-augmented customer service can reduce service costs by up to 30% while improving customer satisfaction.
Training and change management are crucial components of successful human-AI collaboration. Organizations must help staff understand how chatbots complement their roles rather than threaten them, emphasizing how automation of repetitive tasks allows humans to focus on more meaningful, complex work.
Personalization and Emotional Intelligence
Modern AI chatbots are increasingly capable of delivering personalized experiences by analyzing user history, preferences, and behavioral patterns. This personalization extends beyond simply using a customer’s name. Advanced systems can adjust their communication style, recommend relevant products or content, and anticipate user needs based on context.
The development of emotional intelligence in AI chatbots represents a fascinating frontier. While true emotional understanding remains beyond current AI capabilities, chatbots are becoming more adept at recognizing sentiment in user messages and adjusting their responses accordingly. Research from MIT has demonstrated that AI systems can identify emotional states from text with increasing accuracy, enabling more empathetic interactions.
Tone adaptation is another area of advancement. Sophisticated chatbots can detect when users are frustrated, confused, or satisfied, and modify their communication style to match the situation. A frustrated customer might receive more concise, solution-focused responses, while someone exploring options might benefit from more detailed, exploratory dialogue.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The future of AI chatbots lies in their integration with complementary technologies. Voice interfaces powered by advanced speech recognition and synthesis are making chatbots more accessible and natural to use. Gartner predicts that by 2027, chatbots will become the primary customer service channel for roughly a quarter of organizations.
Multimodal capabilities, the ability to process and respond to text, voice, images, and video, are expanding what chatbots can accomplish. A customer could photograph a damaged product and describe the issue verbally, with the chatbot processing both inputs to provide accurate troubleshooting or arrange a replacement.
Augmented reality (AR) integration is opening new possibilities, particularly in technical support and retail contexts. Imagine a chatbot guiding you through furniture assembly via AR overlays or helping you visualize how a product would look in your space while answering questions in real-time.
Measuring Success and ROI
Organizations implementing AI chatbots need clear metrics to evaluate performance and return on investment. Traditional metrics like response time, resolution rate, and customer satisfaction scores remain important, but they should be supplemented with AI-specific measures.
Containment rate, the percentage of conversations handled entirely by the chatbot without human intervention, provides insight into chatbot effectiveness and identifies areas needing improvement. Intent recognition accuracy measures how well the chatbot understands user requests, while fallback rate indicates how often the chatbot cannot provide a satisfactory response.
User engagement metrics, including conversation length, repeat usage, and task completion rates, reveal whether customers find the chatbot valuable. Financial metrics such as cost per conversation, time saved, and revenue impact through sales assistance or upselling help quantify the business value of chatbot investments.
Best Practices for Implementation
Successful AI chatbot deployment requires thoughtful planning and execution. Organizations should start by clearly defining use cases and objectives rather than implementing chatbots simply because competitors have them. Understanding which tasks are best suited for automation and which require human expertise ensures resources are invested wisely.
Designing conversational flows that feel natural while guiding users toward resolution is both an art and a science. Effective chatbots anticipate user needs, offer clear options, and make it easy to escalate to human support when necessary. Master customer service AI chatbots by focusing on user experience throughout the design process.
Continuous improvement based on user feedback and conversation analysis is essential. Organizations should regularly review chatbot interactions, identify common failure points, and refine responses and capabilities. Machine learning models require ongoing training with new data to maintain and improve performance over time.
Transparency about chatbot limitations builds trust with users. Clearly indicating when users are interacting with AI rather than humans and providing easy access to human support when needed demonstrates respect for customer preferences and sets appropriate expectations.
Ethical Considerations and Responsible AI
As AI chatbots become more sophisticated and prevalent, ethical considerations must guide their development and deployment. Bias in AI systems remains a significant concern, as chatbots can inadvertently perpetuate or amplify societal biases present in their training data. Organizations must actively work to identify and mitigate biases in their chatbot systems.
Transparency about data usage and obtaining informed consent for data collection are fundamental ethical requirements. Users should understand what information is being collected, how it’s being used, and have control over their data. The European Union’s AI Act establishes requirements for transparency and accountability in AI systems, setting a precedent that other jurisdictions are likely to follow.
The environmental impact of AI systems deserves consideration as well. Training and running large language models consume substantial energy and computational resources. Organizations should consider the sustainability of their AI implementations and explore ways to minimize their environmental footprint while maintaining performance.
The Road Ahead
The trajectory of AI chatbot development points toward increasingly sophisticated, context-aware, and helpful systems. Advances in multimodal understanding, reasoning capabilities, and personalization will make chatbots more valuable across diverse applications. The distinction between interacting with AI and humans may continue to blur, raising new questions about disclosure and user awareness.
Industry-specific chatbots trained on specialized knowledge will become more common, offering expert-level assistance in fields like medicine, law, engineering, and education. These domain-specific implementations will combine general conversational abilities with deep expertise, providing value that generic chatbots cannot match.
The integration of chatbots into the broader ecosystem of AI tools and business systems will deepen. Rather than standalone applications, chatbots will serve as conversational interfaces to comprehensive AI platforms that orchestrate multiple capabilities, from data analysis to task automation.
Conclusion
AI chatbots have evolved from novelty to necessity in the modern digital landscape. Their ability to provide instant, scalable, personalized assistance makes them invaluable tools for organizations seeking to improve customer experience while managing costs. However, successful implementation requires careful consideration of technical capabilities, ethical implications, and the appropriate balance between automation and human touch.
As technology continues to advance, organizations that thoughtfully integrate AI chatbots into their operations with clear objectives, robust governance, and a commitment to continuous improvement will be best positioned to realize the full potential of conversational AI. The future of chatbots is not about replacing human interaction but about enhancing it, making businesses more responsive, efficient, and customer-centric in an increasingly digital world.