The manufacturing sector is navigating a growing number of challenges: evolving customer demands, intricate software-mechanical product integrations, just-in-time global supply chains that become challenging (again), and a shrinking skilled labor force. Meanwhile, the entire industry is working under intense pressure to improve productivity, manage energy consumption, and keep costs in check. To stay competitive, the industry is undergoing a digital transformation—and data is at the center of that shift.
Generative AI based on data-driven manufacturing offers a powerful answer to many of these challenges. Utilizing existing sensorics, and a broad variety of data sources ranging from enterprise resource planning (ERP) for production to machine specific temperature sensors brings the opportunity to drive new concepts, making the original thought of a Digital Twin so much more valuable.
Picking one prime example: on the shop floor, one of the most critical and high-impact applications of these strategies is predictive maintenance. Downtime isn’t just inconvenient—it’s expensive. Every unproductive hour in the automotive sector now costs $2.3 million (Siemens, The True Cost of Downtime 2024). For manufacturers across all sectors, predictive maintenance is no longer optional, but the foundation of operational excellence and profitability.
At its core, predictive maintenance is about using data to anticipate machine failures before they happen. It began with traditional statistical models, evolved with machine learning, and is now entering a new era of more advanced approaches, including generative AI with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) capabilities. Manufacturers built RAG based solutions focused on enabling faster access to repair, with data from maintenance manuals and then linked to sensors on user/maintainer interactions. While this was originally considered groundbreaking, it became clear that these solutions are reactive versus proactive.
The next frontier is multi-agent systems—AI-powered agents working together to monitor, reason, and act. Agents take real-time operational data and mesh it with existing sources to understand the state of a device or component. They use generative AI for real-time signal processing, encompassing all stages: embeddings, vector search, LLM retrieval, and result reranking. A set of agents acting as a “Digital Expert” can now process like a human from a top line objective (“Maximize the operational uptime”) to a partition of single decision items (“Keep the temperature of the cutting tool at or below 200C”). Each agent then is going through three phases:
- Perceive: The agent receives context and prior information collected and prepared for potential tasks. This could include data on average temperatures, age of tools and other information.
- Decide: The agent puts the prior information and the actual input signals for the specific item (“Ensure optimum parameters for the cutting tool”) into context.
- Act: The agent takes action based on the inputs and the LLM response, initiating changes where needed (“Reduce cutting speed by 10millimeters per second”).
One of the key components for this concept is the real-time capability of accessing any of the relevant data, along with the ability to act. This is where the database and the memory of the agent come into play. For the Digital Expert, its “memory” is comparable to the learning experiences humans “save” in their brain. Some memories are short term, such as the immediate parameters to be set in the actual context, other memory is long term and focuses on the bigger picture, like the best operational condition for a cutting tool based on historical evidence.
On the shop floor agents can automate inspections, re-optimize production schedules, assist with fault diagnostics, and more. According to a LangChain survey, 78% of companies are actively developing AI agents, and over half already have at least one agent in production. Manufacturing companies can especially benefit from agentic capabilities across a great variety of practical use cases.
| Agent Capabilities | Simple Use Case | Medium Use Case | Complex Use case |
| Managing Multi Step Task | Production Scheduling | Supply Chain Orchestration | Multi Stage Machine Fault Diagnostics |
| Automate Repetitive Tasks | Auto-generated Work Orders | Quality Inspection Reports | Data Logging + Compliance |
| Task routing and collaboration | Work Order Routing | Inter-Departmental Collaboration | Recall Coordination |
| Human-like reasoning | Production Re-optimization | Complex Fault DIagnostics | Context-Aware Maintenance Assurance |
Leveraging AI agents in industrial environments presents unique challenges. Integration with industrial protocols like Modbus or PROFINET is complex; governance and security requirements are strict, especially when agents interact with production equipment. Latency is also a concern as AI models need fast, reliable data access to support real-time responses. And furthermore, the immense volumes of data that agents generate and consume requires companies to sustain a data foundation that is reliable and that can quickly scale without sacrificing performance.
Many of these challenges are not new to manufacturers—and the introduction of document-based databases delivers a proven track record of addressing them. Today, industry leaders in the manufacturing and automotive industries are using document-based databases to power critical Internet of Things (IoT) and telemetry use cases. Bosch, for example, uses a document-based database to store, manage, and analyze huge amounts of data to power its Bosch IoT Insights solution. The flexible document model is the ideal data storage solution for diverse sensor inputs and machine telemetry because it seamlessly enables systems to iterate and evolve quickly.
So, what would an agentic system look like for predictive maintenance in the manufacturing industry? Let’s take a look at some of the possible components for building such a solution on a document database.
Building a multi-agent predictive maintenance system
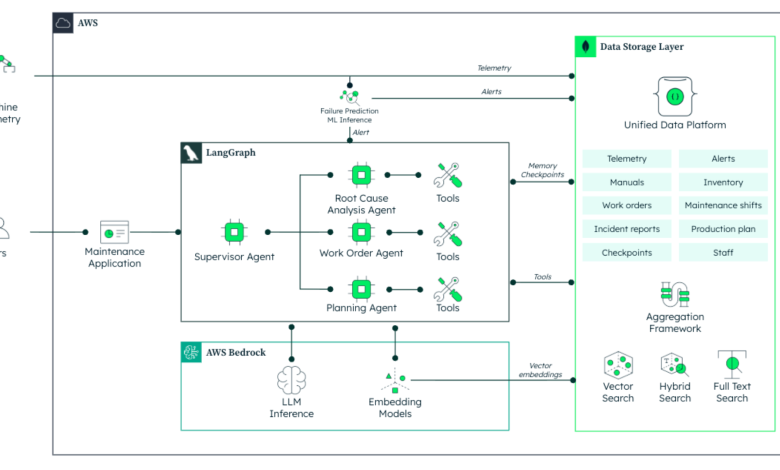
This solution demonstrates how to build a multi-agent predictive maintenance system using a NoSQL document database, an agent orchestration framework, and a managed service for foundational models. This system can streamline complex processes, such as detecting equipment anomalies, diagnosing root causes, generating work orders, and scheduling maintenance. At a high level, this solution leverages the document database as the unified data layer. The agent orchestration framework provides the coordination layer, enabling graph-based interaction among different specialized agents, while the managed service for foundational models powers the underlying LLMs used by the agents to reason and make decisions.
The architecture follows a supervisor-agent pattern. The supervisor coordinates tasks and delegates to three specialized agents:
- Failure agent: which performs root cause analysis and generates incident reports.
- Work order agent: which drafts maintenance work orders with detailed requirements.
- Planning agent: which identifies the optimal time slot for the maintenance task based on availability and production constraints.
High-level architecture of a multi-agent predictive maintenance system.
This modular design enables the system to scale easily and adapt to different operational needs. Let’s walk through the full process in four key steps.
Step 1: Failure prediction kicks off the agentic workflow
The process begins with an alert—something unusual in the machine data or logs that could point to a potential failure. The database provides a unified view of operational data, real-time processing capabilities, and seamless compatibility with machine learning tools. Sensor data is processed in real-time and integrated with ML inference models. All while the downstream applications remain up to date with the latest notifications and dashboards. From there, the supervisor agent takes over and coordinates the next steps.
Step 2: Leverage your data for root cause analysis
The supervisor notifies the failure agent about the alert. Manual diagnostics of a machine can take hours—sifting through manuals, historical logs, and environmental data. The AI agent automates this process. It collects relevant documents, retrieves contextual insights using vector search, and analyzes environmental conditions stored in the database—like temperature or humidity at the time of failure. With this data, the agent performs a root cause analysis and proposes corrective actions. It generates a concise incident report and shares it with the supervisor agent, which then moves the workflow forward.
Step 3: Work order process automation
The work order agent receives the incident report and drafts a comprehensive maintenance work order. It pulls from previous similar tasks to estimate time requirements, identify the necessary materials, and ensure the right skill sets are listed. All of this is pre-filled into a standardized work order template and saved back into the database. This step also includes a human-in-the-loop checkpoint. Technicians or supervisors can review and modify the draft before it is finalized.
Step 4: Finding the optimal maintenance schedule
Once the work order is approved, the planning agent steps in. Its task is to schedule the maintenance activity without disrupting production. The agent queries the production calendar, checks staff shift schedules, and verifies inventory availability for required materials. It considers alert severity and rescheduling constraints to find the most efficient time slot. Once the optimal window is identified, the agent sends the updated plan to the scheduling system.
While we focused on a predictive maintenance workflow, this architecture can be easily extended. Need agents for compliance reporting, spare parts procurement, or shift planning? No problem. With the right foundation, the possibilities are endless.
Unlocking manufacturing excellence with Agentic AI
Agentic AI represents a new chapter in the evolution of predictive maintenance, enabling manufacturers to move from reactive responses to intelligent, autonomous decision-making. By combining AI agents with real-time telemetry and a unified data foundation, teams can reduce downtime, cut maintenance costs, and boost equipment reliability. But to work at scale, these systems need flexible, high-performance infrastructure. With native support for time series data, vector search, stream processing, and more, document-based databases make it easier to build, operate, and evolve multi-agent solutions in complex industrial environments. The result is smarter operations, greater resilience, and a clear path to manufacturing excellence.