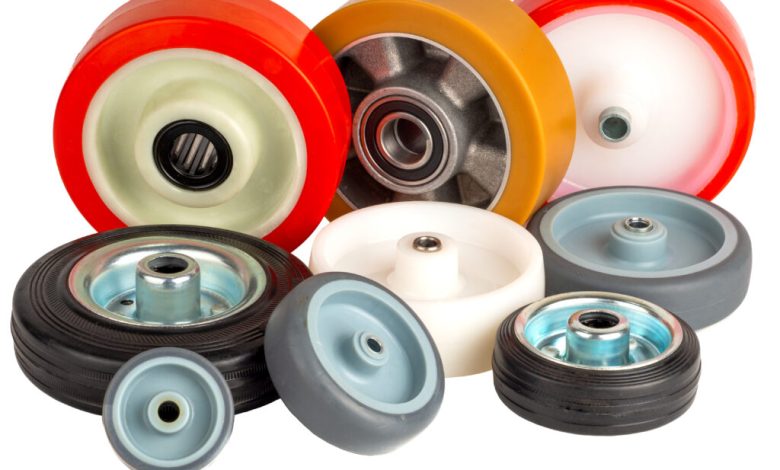
In industrial operations, wheel selection is rarely about preference. It is about load behavior, floor conditions, maintenance cycles, and how equipment performs over time. Facilities that move heavy carts, racks, or machinery every day tend to favor solutions that behave predictably under stress rather than those that optimize for short-term comfort.
This becomes especially relevant in environments where solid rubber wheel industrial applications are common, as wheel performance directly affects uptime, operator control, and long-term equipment wear. The benefits below explain why solid rubber wheels continue to be widely used across demanding industrial settings.
Load Stability Under Continuous Operation
Many industrial wheels spend most of their life under load, not in motion. When equipment remains parked, staged, or partially loaded for long periods, wheel deformation becomes a real concern.
Solid rubber wheels maintain their shape more consistently because:
- They do not rely on internal pressure to support weight
- Load distribution remains stable during extended stationary periods
- Equipment alignment is less likely to drift over time
In solid rubber wheel industrial applications, this stability reduces uneven wear on frames and axles, helping equipment age more evenly.
Fewer Failure Points in Daily Use
Wheel-related failures often create disruption not because they are catastrophic, but because they are frequent. Flats, pressure loss, and casing damage introduce variability into daily operations.
Solid rubber wheels reduce these risks by:
- Eliminating punctures and air-related failures
- Tolerating debris, floor damage, and surface irregularities
- Degrading gradually rather than failing suddenly
For operations that prioritize continuity, solid rubber wheel industrial applications tend to produce fewer unexpected stoppages compared to air-filled alternatives.
Predictable Behavior Across Mixed Floor Conditions
Industrial facilities rarely operate on uniform surfaces. Expansion joints, ramps, patched concrete, and transitions between zones place uneven stress on wheels.
Solid rubber wheels perform reliably because:
- Traction remains consistent without excessive grip
- Vertical compression absorbs minor surface variation
- Directional control is easier to maintain under load
These characteristics are particularly valuable in solid rubber wheel industrial applications, where carts and equipment move repeatedly across the same paths throughout the day.
Lower Maintenance Burden Over Time
Solid rubber wheels simplify maintenance by:
- Removing the need for pressure monitoring
- Allowing wear to be tracked visually and predictably
- Supporting scheduled replacement instead of reactive repair
Over time, solid rubber wheel industrial applications benefit from fewer urgent interventions and more controlled maintenance cycles.
Improved Control and Workplace Safety
Wheel response directly affects how equipment behaves during starts, stops, and turns. Sudden resistance changes or lateral flex can increase the risk of instability, especially in crowded environments.
Solid rubber wheels contribute to safer handling by:
- Maintaining consistent rolling resistance
- Reducing lateral movement under directional changes
- Supporting controlled movement on slopes and ramps
In high-traffic industrial areas, this consistency helps operators maintain control and reduces the likelihood of load shifts or tip events.
Closing Perspective
Solid rubber wheels remain a practical choice because they favor reliability over complexity. Their advantages show up not in isolated specifications, but in how equipment behaves day after day under real operating conditions.
For facilities that value predictable performance, manageable maintenance, and controlled movement, solid rubber wheel industrial applications continue to justify their place in industrial material handling systems.





