The world we live in today is always running low on time and highly thrives on tasks done instantaneously – be it daily life chores or fixing technological discrepancies. The constant need for round-the-clock services in various aspects of our functional society is paving the way for a new era of autonomous systems, the AI Agents. This article dives deeper into how these intelligent entities are designed to perceive their environment, make informed decisions, and execute actions autonomously.
Understanding AI Agents
An artificial intelligence agent is a software program that interacts with the environment, collects data, and then uses it to perform self-determined tasks to meet predetermined goals. The only human intervention it needs is for goal setting, whereas the actions required to achieve that goal are self-determined by the AI agent. Projecting a rapid market growth from USD 5.29 billion in 2024 to USD 216.8 billion by 2035, the AI agents market is set to thrive and revolutionize technology in the coming future. These agents rely on machine learning and natural language processing which allow them to handle tasks ranging from answering simple questions to resolving complex issues to even multi-tasking.
What makes these agents even more interesting is their ability to continuously improve their own performance through self-learning. This function of AI Agents takes them a step ahead of traditional AI, which requires constant human input for specific tasks. For example, consider a contact center AI Agent which is tasked with resolving customer queries. The agent will automatically ask the customer various questions related to their query, search for information in internal documents and workflows, and present a solution. On the basis of customer responses, it then determines if it can resolve the query itself or needs human intervention.
Unraveling the Mechanics: How AI Agents Work?
To understand how AI agents operate, it’s essential to delve into their core components and processes. At the heart of their functionality lies a sophisticated interplay of algorithms, data processing, and decision-making systems. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the functioning of AI agents-
- Interpretation and Information Gathering: The process starts with the AI agents gathering data from various sources, which include customer interactions, transaction histories, and social media. This data plays a crucial role in understanding the context and nuances of the customer inquiries provided. In addition to this, advanced AI agents have the ability to integrate and process data in real time, providing customers with the most up-to-date information to handle inquiries effectively.
- Problem-Solving: AI Agents use sophisticated deep learning models to analyze the collected data and identify patterns, which helps in problem-solving. For example, these agents can determine the most appropriate response for a customer query, based on past interactions and the current context. This process is further enhanced by the agent’s ability to learn from previous experiences and improve its responses over time.
- Execution: After solving the problem, AI agents execute the required action. This could involve answering a customer query, processing a request, or escalating a complex issue to a human agent. The execution is tailored to be efficient and seamless, which ensures the customers receive a timely and accurate response.
A Breakdown of AI Agent Types and Their Architectures
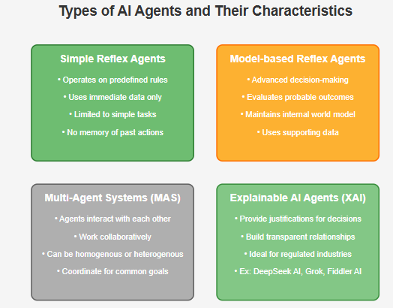
Types of AI Agents
Depending on the architecture, AI agents come in many different forms. Here are a few of them:
- Simple Reflex Agents: A simple reflex agent has an operating system strictly based on predefined rules and its immediate data. It doesn’t respond to situations beyond a given event condition action rule. Hence, making it suitable only for simpler tasks that don’t require extensive training.
- Model-based Reflex Agents: A model-based agent has a more advanced decision-making mechanism that allows it to evaluate probable outcomes and consequences before making a decision, rather than merely following a specific rule. This decision-making process is supported by a perceived internal model of the world, which it builds by using supporting data.
- Multi-Agent Systems (MAS): These agents interact with other agents, working collaboratively to achieve a common goal. They typically coordinate and communicate to achieve a predefined objective. All of these agents can either be homogenous (having the same capabilities and goals) or heterogenous (each with different capabilities or goals) depending on the needs of the business.
- Explainable AI Agents (XAI): XAI agents are relatively recent in the AI agents market, but once established properly, they will have the potential to be revolutionary for heavily regulated industries. These agents provide clear justifications and resources for every decision they make, building a transparent relationship with the consumer. This development is essential for tightly regulated sectors like healthcare, legal, and finance. Prominent examples include DeepSeek AI, Grok and Fiddler AI.
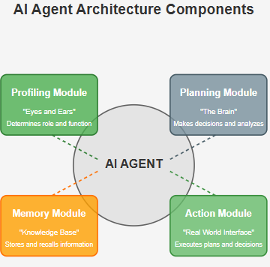
Architecture: The architecture of the AI agents acts as the foundation for its components, principles, and interactions. It’s an essential framework that determines the decision-making, information processing, and environment-perceiving abilities of the agent. It has four main components:
- The Profiling Module: This module works as the eyes and ears of the agent, helping it determine the role or function within a specific context.
- The Memory Module: This module is considered the knowledge base of the agent. It enables the agent to remember details, recall past behaviors, and learn from mistakes.
- The Planning Module: The brain of the AI agent, this module provides it the ability to make decisions, analyze situations, and plan for the future.
- The Action Module: This combines all the information provided by the other modules and puts plans and decisions into action. It connects the agent to the real world.
From the above components, it can be comprehended that altering this architecture can dramatically change how an agent functions in the real world. Let’s dive deeper into some of the variations of AI agent architecture to understand the workings better.
Type of AI Agent Architectures
- Reactive Architecture: AI Agent architecture in its simplest form with no understanding of the world around it. It simply responds to stimuli or changes in the environment in a predetermined way.
- Deliberative Architecture: This architecture has an internal understanding of the world, allowing it to make decisions on the best action to take. As such, deliberative architecture is capable of much more advanced processes and planning.
- Hybrid Architecture: The offspring with the strength of both reactive and deliberative architectures, hybrid allows the intelligent agent to perform both the tasks; autonomous decisions and instant reaction to stimuli.
- Cognitive Architecture: This architecture mimics the human brain as the AI agents built on this framework can learn new skills and improve over time.
Based on the preferred architecture, the actions, reactions and decision-making process of the AI agents can be tailored to suit a wide range of purposes.
Beyond Automation: How AI Agents are Reshaping Industries
AI agents are increasingly being deployed across diverse industries, automating tasks, improving efficiency, and enabling new capabilities. Depending on the specific industry and application, their roles are highly varied. Here are a few of the major industries where AI agents are bringing a revolution:
- Healthcare: AI agents can assist doctors in disease diagnosis by analyzing medical images. They can also build personalized patient treatment plans as well as assist with record management.
- Customer Service: AI agents can analyze customer data to provide personalized service experiences along with handling customer inquiries, providing support, and resolving issues.
- Manufacturing: In the manufacturing industry, AI agents can monitor machinery, which will help in predicting maintenance requirements, and optimizing production processes.
- Retail: By analyzing customer data, AI agents can provide personalized recommendations to customers. In addition to that, they can also optimize logistics, improve delivery times, and reduce transportation costs.
- Finance: Fraud detection and providing customers with personalized finance recommendations are a few of the areas where AI agents can assist customers in the banking sector.
These industries are just at the surface level. AI agents can benefit every industry in the world if deployed ethically, from personal assistants to assembly lines and everything in between.
The Future Industry Trends of AI Agents
The future of AI agents is promising due to the continued technological advances and high investments in the R&D of this sector. Advancements in the following areas can be expected in the future-
- Hyper-Personalization: AI agents will make highly personalized experiences possible with their vast and efficient customer data analysis. This will enable businesses to provide services tailored to individual needs. This will transform how we interact with technology and access information.
- Democratization of Development: AI agents have the abilities to empower non-developers to build applications, making technology more accessible for everyone as well as fostering innovations.
- AI-Driven Software Development: AI agents are poised to revolutionize software development by automating various tasks and enabling new development paradigms. This includes autonomous DevOps, where AI agents manage infrastructure and deployments; hyper-personalization of software; and AI-first architectures, where agents are central to application design.
- Increased Autonomy: In the coming future, AI agents can be expected to become more independent and operate autonomously, making complex decisions with minimal human intervention. This is going to pave the way for new levels of automation and efficiency in various industries.
Opportunities and Challenges in Building Robust and Reliable AI Agents
Opportunities:
AI agents present a landscape brimming with opportunities across numerous sectors. Their capacity to automate complex tasks, enhance decision-making through data analysis, and provide personalized experiences is unlocking unprecedented levels of efficiency and innovation for businesses. Let’s take a look at a few of the opportunities AI agents are providing the business landscape.
- Boosting Efficiency:Automation through AI agents leads to increased productivity and lower operational costs. This enables streamlined processes, optimized resource use, and greater overall efficiency.
- Elevating Customer Satisfaction:AI agents deliver prompt and accurate responses to customer inquiries, resulting in happier customers. They offer round-the-clock support, tailored recommendations, and effective solutions.
- Enabling Scalability:AI agents can manage large workloads simultaneously, making them perfect for scaling operations. They adapt to growing demands and provide consistent performance without human resource limitations.
- Generating Actionable Insights:AI agents analyze vast datasets to extract valuable insights that inform data-driven decisions. This provides a deeper understanding of customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance.
Challenges:
Adopting AI agents also presents potential risks that need careful consideration:
- Technical Vulnerabilities:These include potential errors and malfunctions, security weaknesses, and the possibility of AI agents being exploited for malicious activities like automated cyberattacks.
- Ethical Dilemmas:The autonomy of AI agents raises ethical questions concerning decision-making processes, accountability, and the risk of embedded biases. It’s vital to ensure AI agents are developed and deployed in a manner that aligns with ethical standards and societal values.
- Socioeconomic Impacts:Concerns exist regarding potential job losses as AI agents automate tasks previously done by humans. Addressing the social and economic consequences of AI agent implementation and creating strategies to minimize negative impacts is crucial.
While significant hurdles remain, the compelling opportunities presented by AI agents are fueling intense research, development, and investment. This has led to a surge of exciting discoveries and innovative applications across various industries. Lets dive deeper into the key collaborations, emerging market trends, and groundbreaking findings that are shaping this rapidly evolving landscape.
Inside the AI Agent Explosion: Discoveries, Collaborations, and Market Trends
Market Drivers
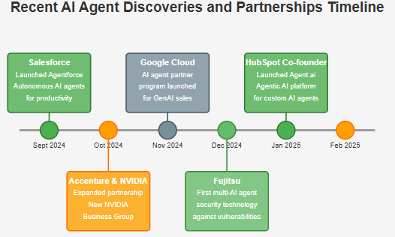
The AI agent market is propelled by a confluence of factors, creating significant momentum for growth and adoption. The increasing demand for automation across diverse industries stands out as a primary driver, pushing businesses to seek solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and streamline workflows. For instance, in November 2024, Google Cloud launched an AI agent partner program to drive GenAI sales, and customer growth. In context to this, Google Cloud’s global channel chief, Kevin Ichhpurani stated that through this program they are enhancing the incentives, product support and co-selling opportunities to help their services and ISV partners bring these solutions to market faster, reach more customers and grow their AI agent businesses.
Labor shortages in key sectors further accelerate this trend, with AI agents offering a viable means to fill critical roles and maintain productivity. Enhanced access to substantial computing power and scalable cloud platforms provides the infrastructure necessary to train and deploy sophisticated AI agent systems. For instance, in November 2024, KOGO launched an AI agent store for enterprises. This store functions like an app store for AI agents and tools, enabling businesses and developers to integrate AI into their workflows and products.
Complementing this is the escalating volume of available data, which is crucial for AI agents to learn, adapt, and refine their performance. Finally, rapid advancements in core AI algorithms, particularly in areas, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning, continuously expand the capabilities and potential applications of AI agents, making them increasingly attractive for businesses seeking innovative solutions.
Recent Findings and Partnerships
- In February 2025, Apaleo launched ‘Agent Hub’, an AI agent marketplace, which enables industry collaboration by connecting property managers, hoteliers, developers, and service providers to accelerate AI adoption.
- In January 2025, HubSpot co-founder launched an agentic AI platform, Agent.ai, designed to enable users to create and collaborate on custom AI agents.
- In December 2024, Fujitsu developed the world’s first multi-AI agent security technology to protect against vulnerabilities and new threats.
- In October 2024, Accenture and NVIDIA announced an expanded partnership, including Accenture’s formation of a new NVIDIA Business Group, to help the world’s enterprises rapidly scale their AI adoption.
- In September 2024, Salesforce launched Agentforce, a suite of autonomous artificial intelligence (AI) agents, to boost employee productivity.
- In September 2024, Salesforce and Google Cloud expanded their partnership to deliver autonomous AI agents. This collaboration will enable mutual customers to deploy autonomous agents with the ability to work in their everyday apps, backed by privacy and user data protection.
The confluence of groundbreaking research, strategic partnerships, and compelling market forces has created unprecedented momentum in the AI agent landscape, paving the way for transformative applications across diverse industries.
Conclusion
AI agents are poised to revolutionize industries by automating tasks, enhancing efficiency, and enabling personalized experiences. Fueled by increasing demand for automation, labor shortages, and advancements in AI algorithms, the AI agent market is experiencing rapid growth. While challenges, such as technical vulnerabilities, ethical dilemmas, and socioeconomic impacts exist, recent findings, partnerships, and market drivers indicate a promising future for AI agents across various sectors, including healthcare, customer service, manufacturing, retail, and finance. With continued innovation and strategic collaborations, AI agents are set to transform how we interact with technology and conduct business.