As digital interactions continue to expand, proxies remain a crucial tool for data access, security, and anonymity. The evolution of proxy servers will be shaped by the increasing need for compliance, enhanced security measures, and AI-driven solutions. Organizations that strategically implement best residential proxies will maintain a competitive edge in accessing, protecting, and utilizing online data effectively.
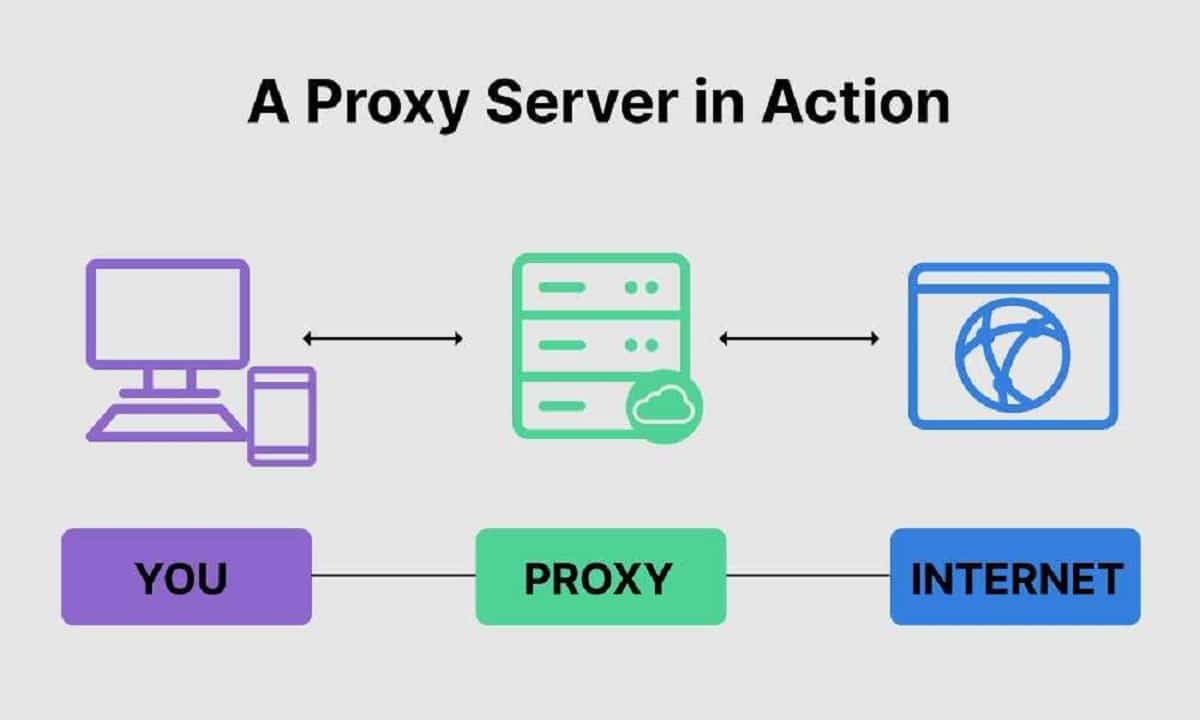
The internet is an ever-evolving environment where privacy and unrestricted access have become primary concerns. Businesses, researchers, and everyday users rely on residential proxies to safeguard online activities and access region-specific data. Unlike datacenter proxies, residential proxies utilize IPs assigned by internet service providers, making them appear as legitimate users.
Different proxy server types serve distinct purposes, from improving security to managing traffic efficiently. Understanding these types helps businesses choose the right proxy solutions for specific needs, whether for data gathering, security, or content verification.
How Best Residential Proxies Function
Residential proxies act as intermediaries, routing user requests through real devices with ISP-assigned IPs. This process allows websites to perceive the user as a real individual rather than a proxy user. Organizations leveraging best residential proxies benefit from improved anonymity, bypassing geo-restrictions, and reducing the likelihood of being flagged or blocked.
Unlike other proxies, residential proxies offer:
- A more legitimate browsing footprint
- Higher success rates for data collection
- Reliable access to region-specific content
Key Proxy Server Types and Their Functions
Forward Proxies
These proxies act as intermediaries for client devices, forwarding requests to the web while masking the user’s identity. Companies use them for security and access control.
Reverse Proxies
Positioned in front of web servers, reverse proxies manage incoming requests, distribute loads, and enhance security by masking backend servers from direct exposure.
Transparent Proxies
Transparent proxies do not modify request headers, meaning the user’s real IP address remains visible. They are often deployed for network monitoring and caching purposes.
Anonymous Proxies
These proxies conceal the user’s IP address, providing a layer of privacy while maintaining access to restricted content.
High Anonymity Proxies
Also known as elite proxies, these completely mask user identities by altering request headers, making online activity nearly untraceable.
Rotating Proxies
Rotating proxies frequently change IP addresses, making them highly effective for web scraping and tasks requiring multiple requests to the same site.
The Demand for Best Residential Proxies: Industry Insights
Recent research highlights the growing reliance on proxies across various industries. Studies indicate that more than 60% of enterprises utilize proxies for competitive analysis and cybersecurity.
- E-commerce companies relying on best residential proxies experience a 25% increase in success rates when extracting pricing data.
- Ad verification firms deploy proxies to confirm correct ad placements and prevent fraudulent activity.
- Financial institutions use proxy server types to monitor transactions and detect suspicious behavior.
Real-World Use Cases for Best Residential Proxies and Proxy Server Types
Web Scraping for Market Intelligence
Companies extract pricing, consumer behavior, and industry trends using residential proxies, ensuring uninterrupted data collection without being blocked.
Ad Verification and Brand Security
Advertisers use proxies to monitor campaign placements worldwide, ensuring that ads appear correctly and are not subject to fraud.
Cybersecurity and Fraud Prevention
High-anonymity proxies enable financial institutions to monitor online transactions securely, protecting user data and detecting potential fraud attempts.
Managing Multiple Accounts in Digital Marketing
Proxies allow businesses to operate multiple social media and e-commerce accounts while minimizing the risk of bans due to suspicious activity.
Addressing the Challenges of Proxy Use
IP Blocking and Detection
As anti-proxy mechanisms improve, websites are better equipped to detect and block proxy traffic. Businesses counteract this with rotating proxies and advanced fingerprinting techniques.
Latency and Speed Concerns
Since residential proxies rely on real user connections, they can experience slower speeds. Choosing a network with a broad IP range helps maintain consistent performance.
Cost vs. Benefit Considerations
Residential proxies tend to be more expensive than datacenter proxies due to their reliability. Organizations must evaluate their proxy usage strategy to justify costs while achieving operational goals.
Emerging Trends in Proxy Technology
AI-Enhanced Proxy Detection Avoidance
With AI playing a growing role in cybersecurity, proxies are evolving to mimic real user behavior more effectively, reducing detection risks.
Decentralized Proxy Networks
Blockchain-based proxy solutions offer decentralized alternatives, making censorship circumvention more accessible and resilient.
Integration with Zero Trust Security Models
Zero Trust frameworks increasingly incorporate proxies to enforce stricter access control and improve enterprise-level cybersecurity.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
With stricter data privacy laws, businesses are leaning towards ethically sourced residential proxies that comply with legal standards.
The Future of Proxy Server Types and Their Impact
As digital interactions continue to expand, proxies remain a crucial tool for data access, security, and anonymity. The evolution of proxy server types will be shaped by the increasing need for compliance, enhanced security measures, and AI-driven solutions. Organizations that strategically implement best residential proxies will maintain a competitive edge in accessing, protecting, and utilizing online data effectively.