IT support has always been a waiting game. Slow laptops, VPN problems, and broken apps clog helpdesk queues and slow down productivity. Our engineering team wanted to change that story — not by adding more people, but by building systems that fix themselves.
The Starting Point
What started with a few ServiceNow workflows soon became something much bigger. Using integration tools like Workato and Nexthink, we taught our systems to detect and fix common problems automatically. When a device ran low on disk space, it cleaned itself. If a VPN failed, it rebooted the network service.
- Chart showing ticket routing before automation.
Measuring Early Automation Success
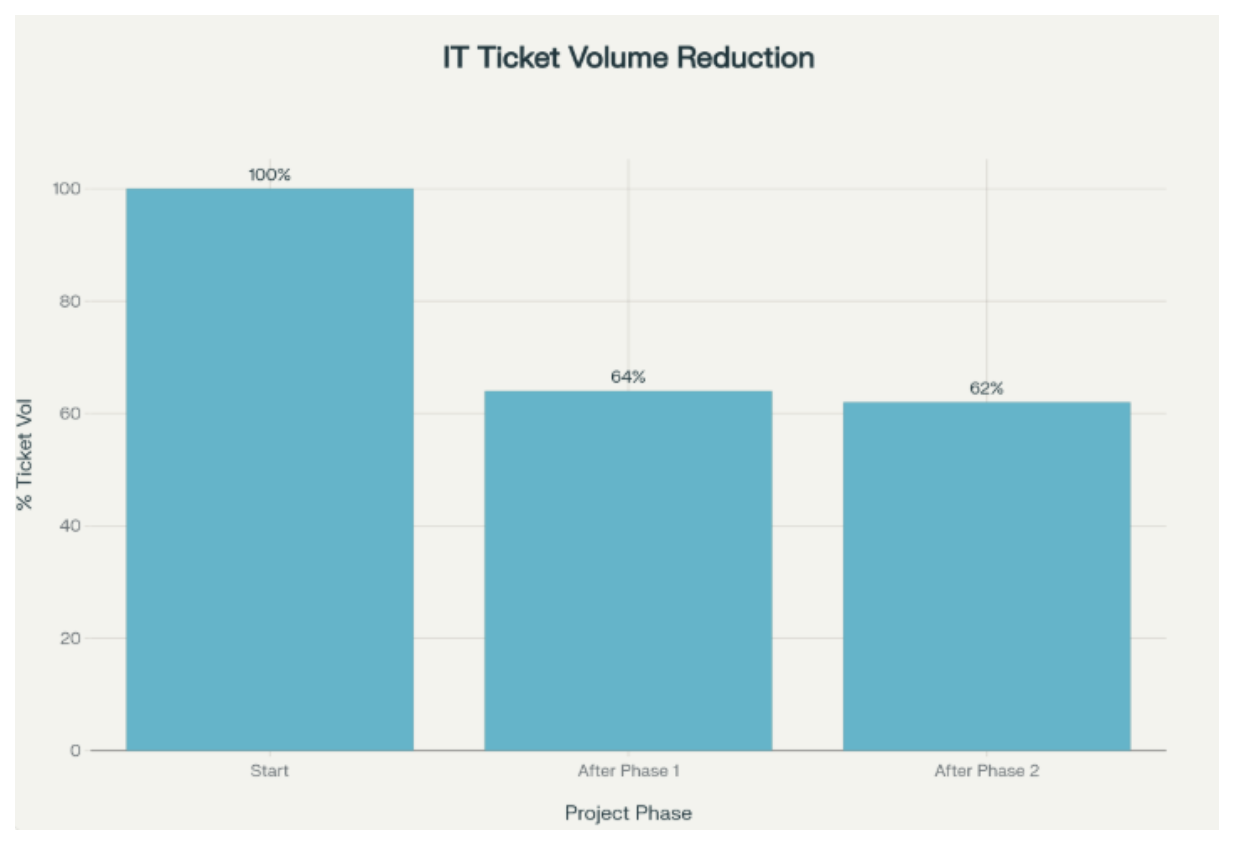
By automating these simple, repeatable tasks, we removed thousands of recurring tickets and cut our support load by more than a third.
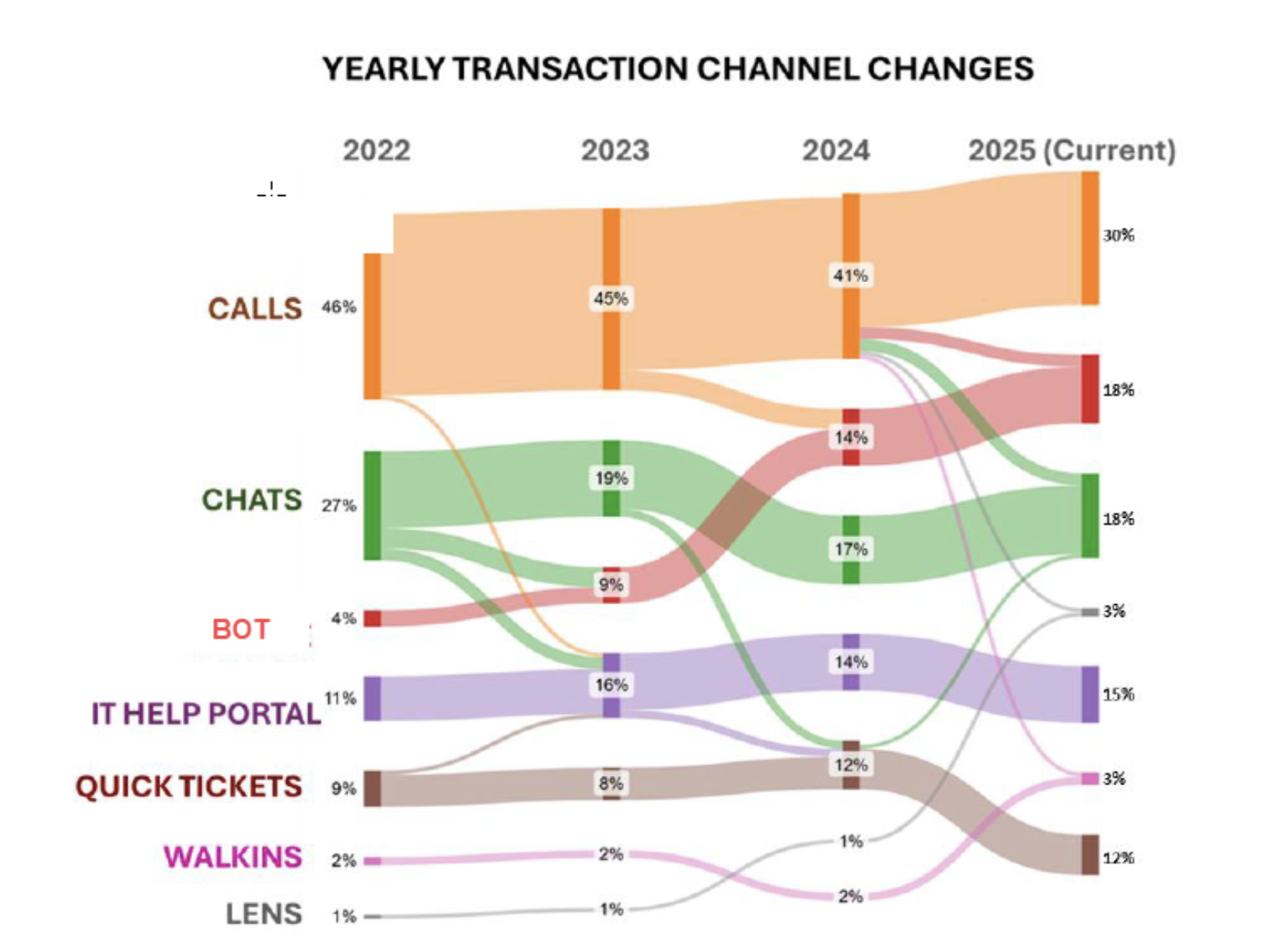
Insert chart: Reduction in IT ticket volume across phases of automation deployment.
Reduction in IT ticket volume across phases of automation deployment
Building the Unified Bot
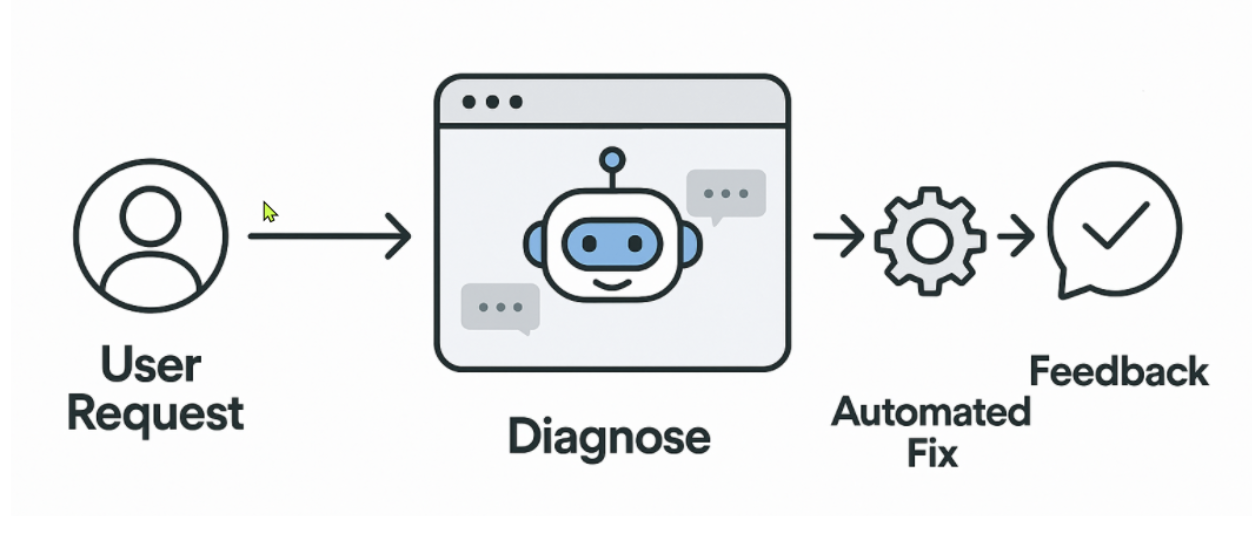
The turning point came when we created one unified bot: a single interface where employees could get help. The bot could chat with users, diagnose issues, trigger repairs, and log everything into ServiceNow. It handled everything from Teams cache resets to disk cleanup, all automatically.
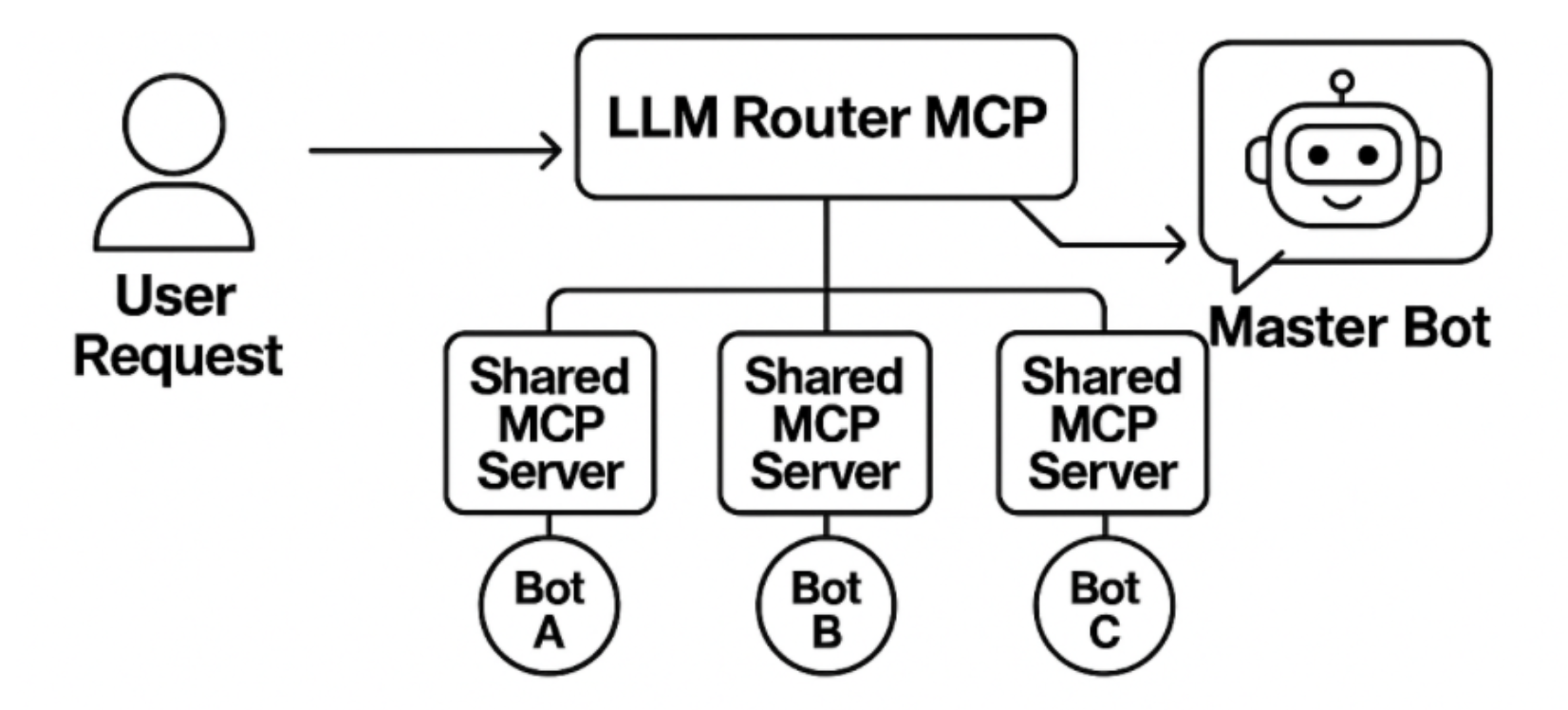
Scaling Up with MCP Servers
The architecture introduces a Master Bot as the primary interface for user interaction. When a user submits a request, the Master Bot receives it and passes it to the LLM Router MCP, which acts as the central orchestrator. The router intelligently determines which Shared MCP Server should handle the task. Each MCP server manages its own set of specialized bots, enabling targeted workflows and automation. The process follows three steps:
- Routing and Orchestration – The Master Bot forwards the request to the router, which selects the best MCP for the job.
- Execution – The chosen MCP activates the appropriate bot to perform the required action.
- Response – Feedback flows back through the MCP and router to the Master Bot, which delivers the result to the user.
This layered method ensures scalability, modularity, and smooth integration across different automation environments.
The Impact
Here’s what changed in our IT world:
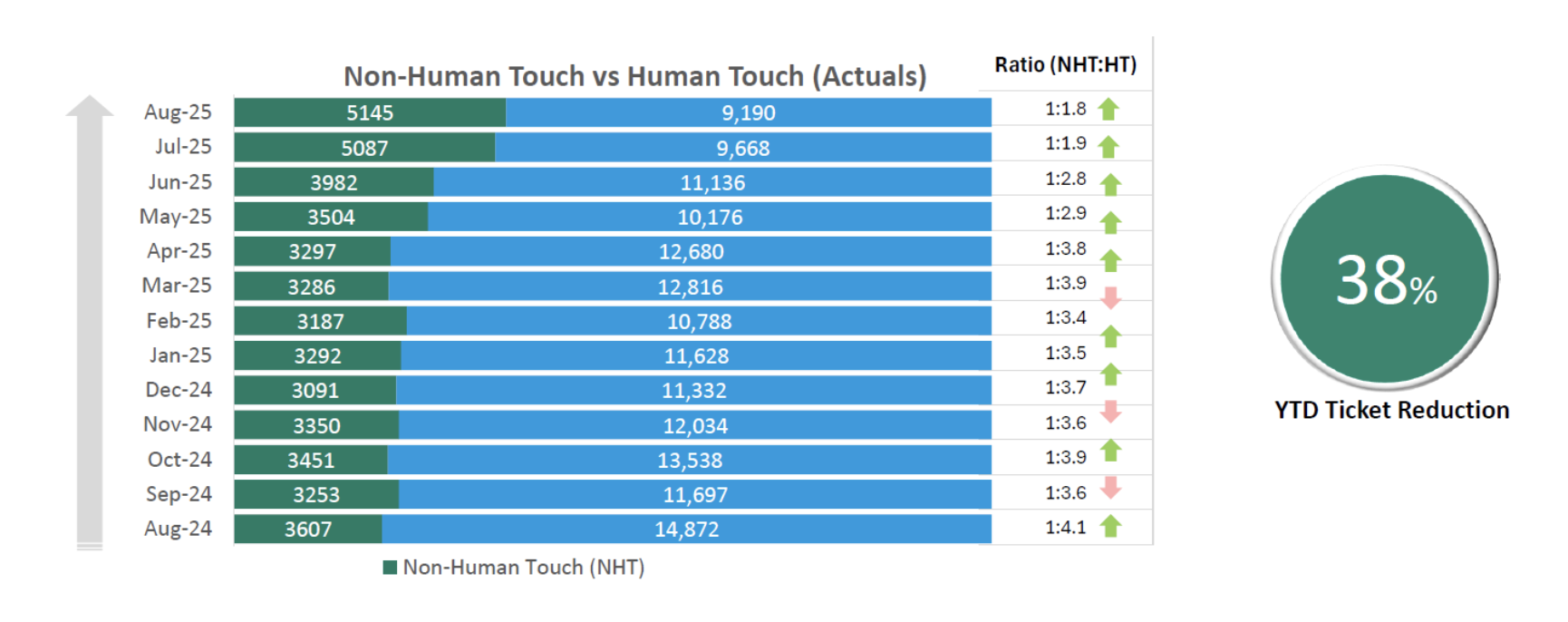
- 38% fewer tickets reach human agents.
- 2,700 automated device repairs have run.
- Over 800 user hours saved this year.
- User happiness scores are way up.
Getting Started with AI Bots in Any Company
This journey isn’t unique. Any company, whether large or small, can begin their path with just a few bots for key IT tasks. As you automate more, you can unify these bots under a central system and gradually introduce smarter collaboration—eventually shifting to a fully self-healing, zero-touch helpdesk.
Conclusion
Zero-touch IT isn’t about removing people from the equation. It’s about giving them time back for creative, human work — while machines quietly handle the rest. The journey from manual to automated support is an investment, but the rewards are visible every day when IT issues resolve themselves before anyone even notices.
Microsoft, “AI-powered success—with more than 1,000 stories of enterprise innovation,” 2025. [Online]. Available:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/ai/ai-lab-case-studies
McKinsey & Company, “AI in the workplace: A report for 2025,” 2025. [Online]. Available:
https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/artificial-intelligence/ai-in-the-workplace-report-2025/
Top Enterprise Automation Tools for 2025,” 2024. [Online]. Available:
https://frends.com/en/blog/enterprise-automation-best-tools-2025
AI‑Driven Automation: 7 Real‑Life Business Success Stories,” 2025. [Online]. Available:
https://www.inapps.net/blog/ai-automation-real-life-success-stories/