The significant processing unit (CPU) is regularly known as the “mind” of a laptop, and just like an organic mind, it needs to be kept in a stable environment to function optimally. As the CPU performs complicated calculations, it generates warm temperature, and if this heat is not well dissipated, it could bring about a number of problems, from overall performance throttling and device instability to permanent hardware damage. Knowing the manner to control CPU temperature is a vital capacity for any laptop man or woman, and it includes a combination of hardware answers, software monitoring, and regular safety.
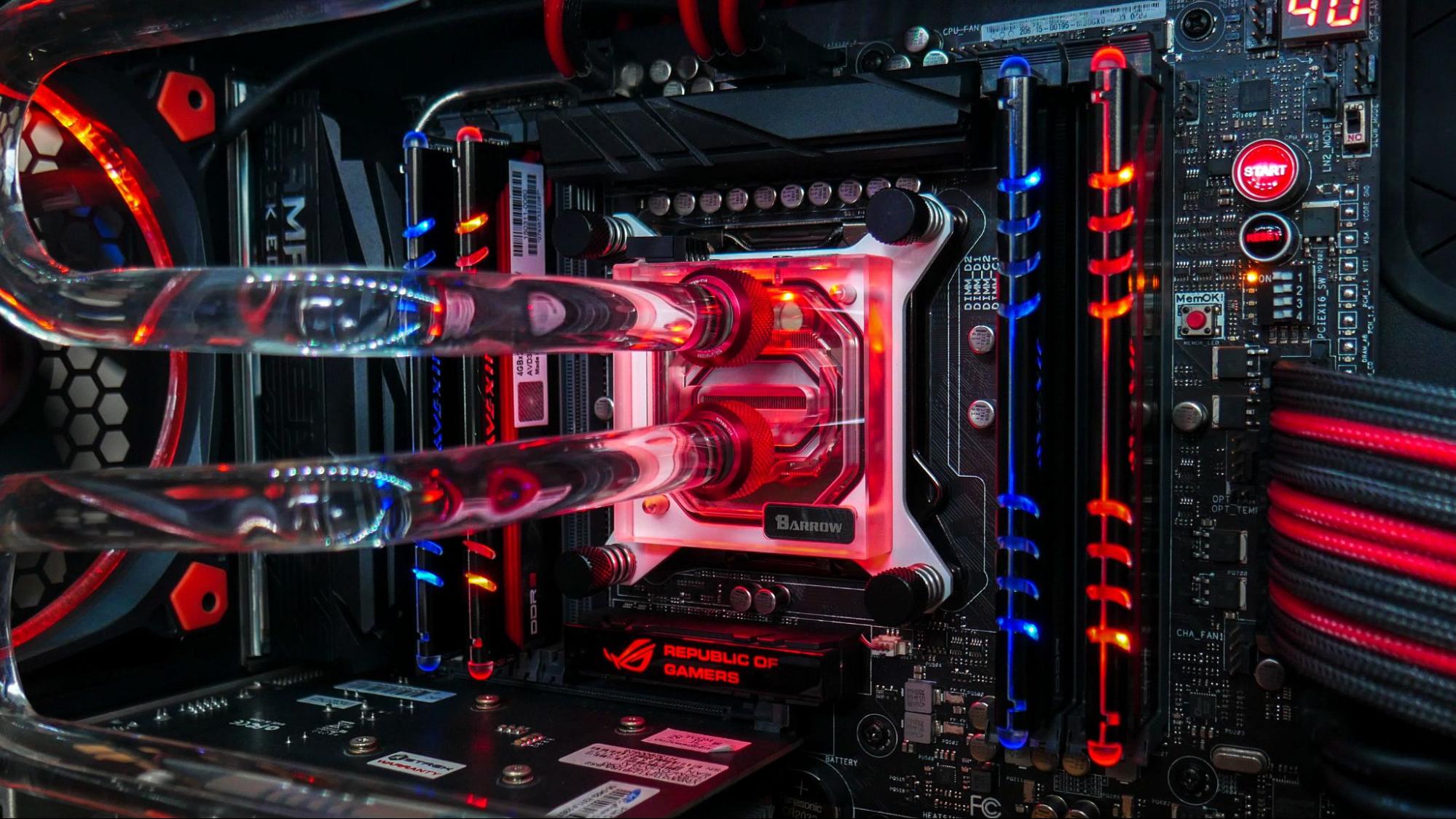
The Role of Cooling Hardware
At the maximum basic stage, your computer’s cooling system is responsible for removing heat from the CPU. Every current processor comes with a stock cooler, which is an aggregate of a heatsink and a fan. The heatsink is a block of metal, commonly aluminum or copper, that attracts heat from the CPU. The fan then blows air across the heatsink is a block of metal, commonly aluminum or copper, that attracts heat from the CPU. The fan then blows air across the heatsink’s fins to cool it down. A critical issue in this setup is thermal paste, a conductive compound implemented between the CPU and the heatsink.. This paste fills in microscopic gaps between the two surfaces, ensuring green warmth transfer. Over time, thermal paste can dry out and lose its effectiveness, so reapplying it every few years may be a simple yet powerful way to enhance cooling. For users with high-performance CPUs or those who interact in stressful tasks like gaming or video editing, a fundamental stock cooler won’t be enough. Upgrading to a more robust air cooler with a larger heatsink and greater effective fanatics, or even a liquid cooling machine (AIO or custom loop), can dramatically lower temperatures and provide better overall performance under heavy load.
Software Solutions and System Optimization
Beyond the physical hardware, the software program performs a significant role in temperature control. The first step is to display your CPU’s temperature with a dependable 0.33-celebration software. Tools like Core Temp, HWMonitor, or NZXT CAM provide real-time readings, permitting you to appearance how your CPU is performing under special workloads. A regular idle temperature for a CPU is usually between 30-forty five°C, even as temperatures under heavy load are preferably live under 80°C. Consistently exceeding this threshold can suggest trouble. Many motherboards also let you control fan speeds at once through the BIOS or a producer’s software. By growing a custom fan curve, you may adjust fan speeds to be more competitive at better temperatures, ensuring that extra air is moved whilst it is wanted maximum. You can also optimize your running system by removing useless history applications and performing normal malware scans, as rogue methods can silently consume CPU resources and generate extra heat.
The Importance of Airflow and Maintenance
Even the most effective cooling device can’t work correctly without out right airflow. A computer’s case is designed to create a glide of air, with intake fans pulling cool air in and exhaust lovers pushing warm air out. Poor cable management, wherein wires obstruct the course of airflow, can create warm spots and prevent heat from escaping. Organizing cables with zip ties or Velcro straps can make an exceptionally huge difference. Additionally, a PC’s environment topics; putting a laptop in an enclosed area or against a wall can block its vents and entrap heat. Laptops, specifically, can benefit from a cooling pad or stand that elevates the device to permit higher air circulation underneath. Finally, recurring cleansing is possibly the most left out however maximum important thing of temperature management. Dust acts as an insulator, trapping heat and clogging fans and heatsinks. Using compressed air to smooth out your pc every few months can take away this debris and repair your cooling system’s performance. By implementing those practices, you can make certain that your CPU stays inside a safe running range, extending its lifespan and preserving high performance for future years.