A global bank spent 18 months building rule-based data pipelines to detect fraud patterns. Their engineers wrote 50,000 lines of code to flag suspicious transactions. A generative AI model trained on the same data now identifies twice as many fraud cases in real time and adopts new schemes without code changes.
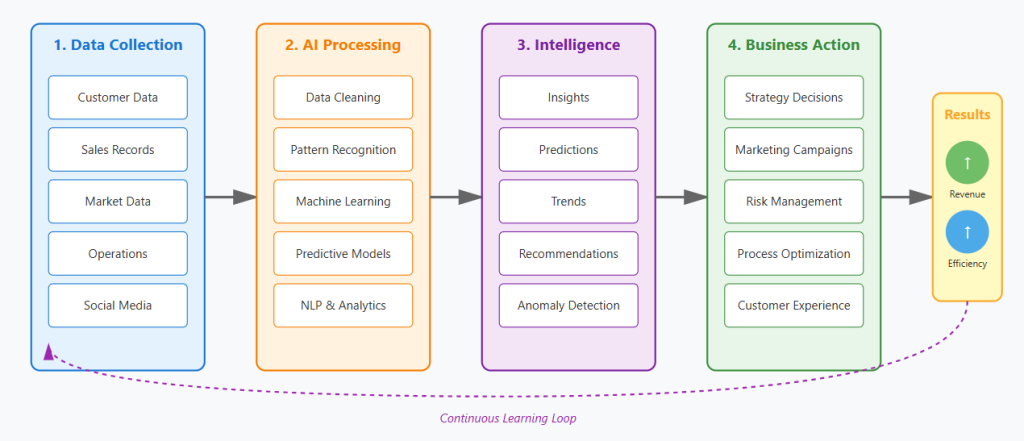
How AI-driven data intelligence works in business
The New Economics of Data Engineering
Companies own the data they need, but can’t use it. Information sits scattered across dozens of systems while AI projects stall at the starting line. The tools that created this problem are now solving it.
Data sprawl—the hidden tax on AI projects
Companies create data in dozens of systems. Customer records live in Salesforce. Transaction logs sit in PostgreSQL. Marketing analytics run through Google Analytics. Product usage data streams into Snowflake. Each team picks its own tools and storage. AI models need unified data to train properly. Data sprawl means engineers spend 60% of project time just finding and connecting sources before AI work begins.
Data intelligence—making sense of what you already own
Data intelligence is the practice of extracting business value from information assets. It combines analytics, machine learning, and automation to answer questions that drive decisions. A retail chain uses it to predict inventory needs by store location. A bank applies it to spot loan applicants likely to default. The process starts with collecting data from multiple sources. Software then cleans, structures, and analyzes that data. Patterns emerge that humans miss in manual reviews. The output is actionable: raise prices in market A, hire staff for shift B, or contact customer C before they churn. Data intelligence turns spreadsheets into strategy.
What AI changed in data engineering
AI-driven data engineering services automate tasks formerly required manual coding. Traditional data engineers wrote scripts to clean messy data, fix errors, and transform formats. They built pipelines by hand, rule by rule. AI models now detect data quality issues automatically. They suggest transformations based on patterns in the data itself. Schema mapping that took weeks now happens in hours. Generative AI writes integration code from plain language descriptions. Machine learning monitors pipelines and fixes breaks without human involvement. The shift is from building infrastructure to training systems that build themselves. Data engineers now spend time on strategy instead of syntax.
Deloitte uses a disciplined strategy to integrate and modernize enterprise data on Databricks’ data intelligence platform. The alliance bridges data lakes and warehouses to support unified analytics and AI workloads. Cloud data infrastructure modernization supports optimization, governance, and AI-enabled insights.
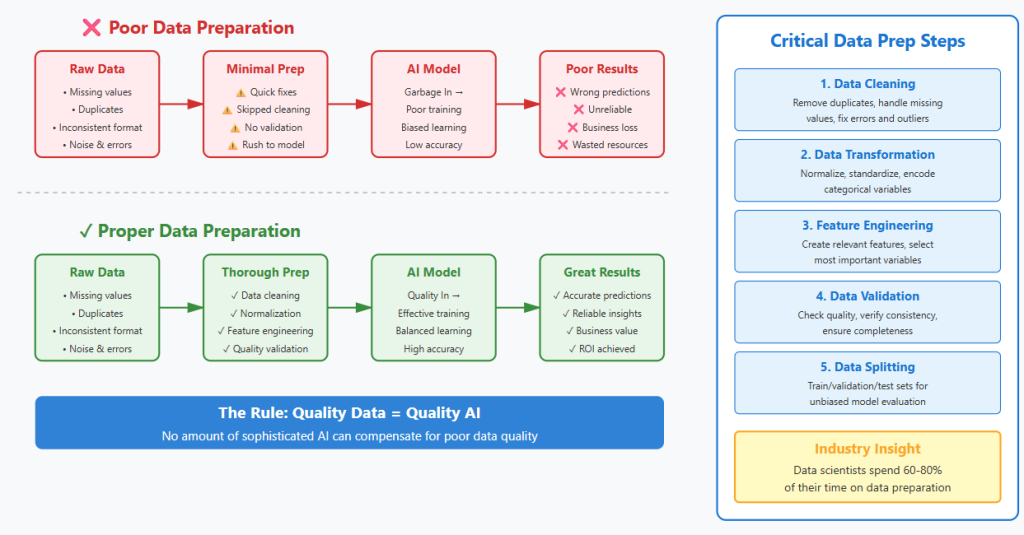
Why Data Prep Decides AI Success
Companies spend millions on advanced models but overlook the foundation. Poor data quality is the main cause of AI project failures. The fix requires pipelines that clean, structure, and validate information before any model sees it.
AI data engineering components
- AI data engineering automates the task of cleaning messy datasets.
- These services use machine learning to map fields between different databases.
- Computers find data faults faster than human workers can.
- AI algorithms detect patterns that show when a system might fail.
- Engineers set up pipelines that fix themselves when a data source changes.
- The tools label millions of records for training new models.
- A central system tracks where all pieces of data come from.
- This automation cuts the time used for manual coding by half.
- Security tools scan for private information to meet legal rules.
- The goal is a reliable stream of facts for the business.
Data quality over models
Leaders often focus on the choice of an LLM. Model selection accounts for only 20% of the total project success. Why is the model less important than the data? Data preparation defines the remaining 80% of the project outcome. Raw data contains noise and errors that often confuse AI systems. Engineers spend weeks fixing dates and removing duplicate records in databases. The AI produces false answers when the input data is poor. Teams must build pipelines to feed fresh data into the system daily. The best model fails if the underlying data lacks quality. Data preparation forms the base for a useful AI tool.
Building data pipelines for AI
Data preparation for these projects follows a set of mechanical steps to convert raw facts into useful inputs. Engineers first pull data from sources like cloud buckets and SQL databases. They remove duplicate records to keep the training set small and accurate.
- Teams strip away HTML tags and junk characters from text files.
- Scripts fix spelling errors and inconsistent date formats in every table.
- The system removes private names and credit card numbers for safety.
- Large documents get broken into smaller chunks for the model to read.
- Computers convert text into lists of numbers called embeddings.
- Analysts check these embeddings for bias or hidden errors.
- The team stores the finished data in a specialized vector database.
- Metadata tags get added to help the system find facts faster.
- Automated tests verify that the data is identical to the initial source.
- The final pipeline feeds clean data into the AI model continuously.
Why data preparation is the foundation of AI success
From Code-Heavy Pipelines to Self-Learning Systems
Traditional ETL requires armies of engineers to hand-code every data transformation. Each new source adds months of development and upkeep burden. Modern data intelligence platforms automate what used to take teams and turn pipeline creation into a configuration task.
The legacy manual assembly line
ETL stands for extract, transform, load. Engineers pull data from source systems on a fixed schedule. They write custom scripts in Python or SQL to clean and reshape each dataset. Rules get coded by hand to handle every foreseen data format. The converted data lands in a central warehouse like Oracle or Teradata. Each new data source requires weeks of development work. Changes to source systems break the pipeline until someone rewrites the code. Testing happens manually before each deployment. The process is predictable but slow. A typical ETL project takes three to six months from start to production.
Self-learning pipelines
Data intelligence platforms ingest streams from APIs, databases, and file systems nonstop. Machine learning detects schema changes and adjusts pipelines automatically. The system handles unstructured content like PDFs, images, and audio files directly. Text gets parsed and converted into vector embeddings for semantic search. These embeddings live in specialized vector databases like Pinecot or Weaviate. AI models classify documents, extract entities, and tag content automatically. Data quality checks run in real time, detecting irregularities as they appear. Engineers define goals in plain language instead of writing transformation code. The platform learns from corrections and improves its own validity over time. Deployment takes days, not months.
Traditional ETL vs. Data Intelligence
Traditional systems only handle structured data like numbers and dates in rigid tables. Generative AI requires unstructured data like text, audio, and video files to function. Legacy pipelines lack the speed to process these large files immediately for training purposes. Why does this stall progress? Rigid schemas prevent engineers from adding new data types quickly. This limitation creates a massive delay in moving AI projects from testing to production.
| Metric | Traditional ETL | Data Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Time to production | 3-6 months per source | Days to weeks |
| Development cost | $150K-$500K per pipeline | $30K-$100K per pipeline |
| Maintenance burden | Manual fixes for each break | Self-healing pipelines |
| Data types supported | Structured tables only | Structured and unstructured |
| Adaptability | Requires code rewrite | Learns from changes |
| Staff required | 3-5 engineers per project | 1-2 engineers per project |
| Error detection | Batch checks, often delayed | Real-time monitoring |
| Business agility | Requests queued for months | New sources added in days |
| ROI timeline | 12-18 months | 3-6 months |
| Scalability | Linear cost with volume | Sub-linear cost with volume |
Companies That Turned Data into Concrete Profit
Data intelligence delivers returns across industries when applied to specific business problems. A retailer, a lender, and a hospital each dealt with expensive gaps in their operations. Predictive systems filled those gaps and generated millions in savings within months.
How a fashion retailer cut inventory waste by $4.2 million
Pain: A mid-sized online clothing retailer carried 30% excess inventory across 200 SKUs. Their buyers relied on last year’s sales data and gut instinct to order stock.
Solution: The company deployed a data intelligence platform that analyzed purchase patterns, return rates, and browsing activity spanning 18 months. The system predicted demand by item, size, and region two weeks ahead. Buyers adjusted orders based on these forecasts instead of annual averages.
Result: Overstock dropped from 30% to 11% within one quarter. The company saved $4.2 million in carrying costs and markdowns in year one.
How a digital lender approved 40% more loans without adding risk
Pain: A fintech company rejected 35% of loan applications because traditional credit scores missed self-employed applicants and gig workers. Their underwriters had no reliable way to assess revenue reliability for non-traditional employment.
Solution: The company implemented a data intelligence system that analyzed bank fraud patterns, invoice frequency, and payment histories. The platform identified reliable borrowers who failed conventional credit checks.
Result: Approval rates increased from 65% to 91% for the target segment. Default rates stayed flat at 2.1%. The lender added $127 million in loan volume within eight months.
How a hospital network reduced readmissions by 31% in six months
Pain: A regional hospital system faced $8 million in annual penalties for high readmission rates among heart failure patients. Doctors lacked visibility into which discharged patients needed rapid follow-up care. Solution: The network deployed a data intelligence platform that analyzed patient vitals, medication adherence, and social determinants from electronic health records. The system detected high-risk patients within 24 hours of discharge. Care coordinators called these patients daily for the first week and arranged home visits when needed.
Result: Readmissions dropped from 19% to 13% across 2,400 patients. The hospital avoided $5.1 million in penalties and superior patient care outcomes measurably.
How a SaaS company cut customer acquisition cost by 43%
Pain: A B2B software company spent $850,000 quarterly on paid ads across six channels with no clear view of what drove conversions. Their marketing team attributed success to last-click metrics that ignored the full customer journey.
Solution: They deployed a data intelligence platform that tracked every touchpoint from first ad impression through contract signature. The system identified that webinar attendees who read two specific case studies converted at 8x the rate of other leads. Marketing reallocated budget to promote those assets and target similar prospects.
Result: Cost per acquisition dropped from $3,200 to $1,820 within two quarters. Revenue per marketing dollar increased by 76%.
Who Writes Your Pipelines When AI Does It Better?
Manual data engineering hit a wall when pipelines grew from 5 sources to 50. Engineers now maintain code instead of building new systems. AI took the repetitive work and is learning to make design decisions on its own.
Data pipelines now need intelligence
Modern pipelines handle 50 data sources, where legacy systems managed five. Unstructured content like PDFs, videos, and chat logs now outnumber structured database records by ten to one. Real-time APIs replace nightly batch jobs, forcing systems to process changes every second. Vector embeddings and semantic search add computational layers that traditional ETL never required. Manual coding can’t keep pace with this complexity.
AI as your data engineering partner
AI now writes transformation code from written descriptions of what you need. The system suggests schema mappings through analyzing sample data from new sources. Machine learning spots data quality issues and proposes fixes without waiting for human review. Engineers review and approve recommendations instead of coding every rule from scratch. The AI learns from each correction and improves its suggestions over time.
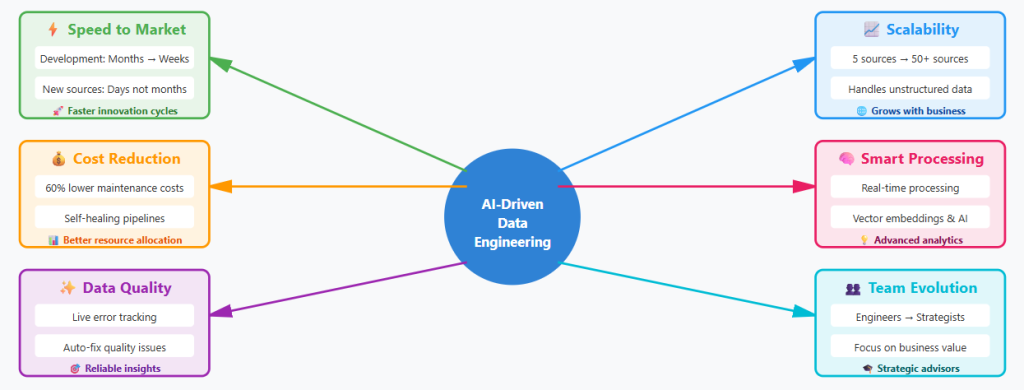
What AI-driven engineering delivers
- Development time drops from months to weeks for new data sources.
- Maintenance costs fall by 60% as self-healing pipelines fix breaks automatically.
- Teams process unstructured content like documents and images without custom code.
- Live tracking catches errors before they corrupt downstream systems.
- Engineers shift from writing boilerplate code to solving business problems.
From plumbing to architecture
Engineers stop debugging ETL scripts and start designing data strategies. They spend time choosing which business questions to answer instead of fixing broken pipelines. Teams experiment with new data sources in days rather than waiting months for resources. Innovation periods accelerate when grunt work disappears. The shift turns data engineers into strategic advisors who shape company direction.
When your code starts writing itself
AI started as a narrow automation tool for repetitive tasks. It now makes decisions about data quality and pipeline architecture. The systems are modified for varying business needs without reprogramming. Future versions will propose new data sources based on gaps in analysis. AI is becoming a collaborator that understands context and suggests strategy.
Key business deliverables from AI-driven data engineering
Three Shifts That Will Redefine Data Engineering
Autonomous pipeline management will become standard across enterprise systems. AI agents will detect new data sources, propose integration plans, and execute them with minimal human approval. Systems will negotiate data formats between applications without manual schema mapping. Self-optimization will tune performance based on usage data and cost constraints. Engineers will set business rules and guardrails while AI handles implementation details.
Natural language will replace code as the primary interface for data tasks. CTOs will describe what they need in plain English and receive working pipelines in hours. The system will seek further details when requirements are ambiguous. Non-technical staff will build their own data products without writing SQL or Python. This increased inclusivity will shift data engineering from a bottleneck to a self-service function.
Streaming data intelligence will merge with operational systems directly. AI will make decisions inside applications instead of feeding dashboards for humans to review. A supply chain system will auto-adjust orders based on demand predictions. Customer service platforms will route calls based on churn risk scores. The boundary between data engineering and application development will disappear.
Forbes highlights data quality, accessibility, and completeness as top constraints for AI adoption. Agentic AI (AI systems that act with limited human input) is changing data profiling, quality checks, and integration in data engineering practices. LLM-powered assistance is boosting discovery, SQL generation, and troubleshooting in data operations. A modern data strategy should unify data sources, enhance governance, and build internal AI and data capabilities.
Turn Your Data into Working Capital
Companies treat data like a storage problem instead of a revenue source. Terabytes sit in warehouses while executives make choices based on instinct. AI-driven data engineering turns that dormant information into working capital. The services automate the grunt work of cleaning, structuring, and connecting disparate sources. Machine learning finds patterns that spreadsheets and SQL queries miss completely. Real-time pipelines feed fresh insights to operational systems automatically. Engineers design strategies instead of debugging broken ETL jobs. The transformation happens in weeks rather than the months traditional projects require. Teams see measurable returns within the first quarter of deployment. Data becomes an asset that appreciates rather than a cost center that drains budgets.