That’s all it takes in 2025 to clone someone’s voice, create a convincing deepfake video, and drain a corporate bank account.
Deepfake technology used to be a Hollywood-level studios and months of work now happens faster than our morning coffee break.
In 2025, deepfake technology has reached a terrifying milestone. Over 8 million synthetic media files are now circulating online, up from just 500,000 two years ago.
And let’s not even start with the financial toll.
Companies are losing an average of $500,000 per deepfake incident, with AI-driven fraud projected to cost U.S. businesses $40 billion by 2027.
Even more alarming… human reviewers can only detect high-quality deepfake technology videos 24.5% of the time.
This means 3/4 fakes slip through unnoticed.
Welcome to 2025. Today, deepfake technology has become the most sophisticated weapon in cybercrime.
In this blog, we’ll break down how deepfake technology works, the new formats emerging in 2025, and why traditional detection methods are no longer enough.
You’ll also see how AI-powered defense systems are helping organizations fight back and so much more.
Let’s get started.
- Deepfakes started as harmless entertainment on Reddit but have evolved into tools for large-scale scams, political manipulation, and corporate fraud.
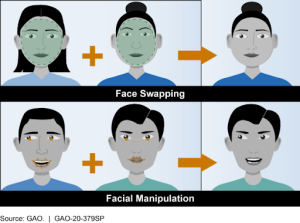
- Current deepfake technology formats include face-swapping, voice cloning, lip-syncing, and full-body reenactments.
- Emerging formats include AI-generated document forgery and biometric spoofing to bypass ID and voice verification systems.
- Deepfake technology can be used in financial fraud, executive impersonation, political disinformation, and personal extortion.
- Traditional deepfake detection methods like manual spotting or forensic tools are no longer effective against modern, real-time deepfakes.
- Only adaptive, AI-powered systems like TruthScan can detect zero-day deepfakes, offering real-time protection across video, audio, and text.
What Is Deepfake Technology?
Deepfake technology means creating something that isn’t real, but looks and sounds completely real. These are AI-generated images, videos, or audio clips that show people or events that never happened.
So, does that mean they’re just like traditional editing?
Not really.
- Traditional editing is what video editors have been doing for decades. It includes cutting, splicing, color correcting, and adding visual effects manually. It uses software tools like Photoshop or Premiere Pro.
- Deepfakes automate that process. They use AI models that can study thousands of images of a person’s face, and then generate new, realistic movements or expressions that were never recorded.
For Example:
In a deepfake, the AI can swap one actor’s face with another’s, match every blink and expression, and even make them say words they never spoke.
Now, before we get into how this deepfake technology works, let’s look at where it all began.
The word “deepfake” comes from combining “deep learning” and “fake.”
It first appeared in 2017, when a Reddit user created a community to share AI-generated videos.
Soon after, open-source tools like DeepFaceLab, FakeApp, and ZAO made it possible for almost anyone to create realistic deepfakes in minutes. Today, DeepFaceLab alone powers over 95% of all deepfake videos online. And it no longer takes a high-end computer or coding expertise. With just a short voice clip and a few dollars, anyone can impersonate another person online.
Now, let’s get to the question that “how does DeepFake technology work?”
Deepfake technology rely on two key AI models: Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs).
- GANs work like a digital face-off. One AI (the generator) tries to create fake content, while another (the discriminator) tries to catch it. With every round, both improve, until the fake becomes nearly impossible to detect.
- VAEs, on the other hand, are more like careful students of reality. They learn the patterns, lighting, and facial details of real people by compressing and reconstructing images over and over. The more they practice, the more natural their recreated faces look.
VAEs act as the foundation. They teach the system how real faces look, move, and react to light. Once that understanding is built, GANs refine the output. It sharpens details, smooths motion, and perfects expressions until each frame appears convincingly real.
Common Formats: Video, Audio, Images, and Text
Deepfake technology isn’t limited to videos. They can exist in almost every format we use online.
AI can manipulate sound, visuals, and even written words to create synthetic versions of reality.
Let’s break down how each format is being used.
| Format | Description | Example | Sources |
| Video | AI-generated videos that mix fake visuals and audio through face-swapping or performance transfer. | In 2024, scammers posed as an Arup executive in a live video call, using deepfakes to steal $25.6M. | Source |
| Audio (Voice Cloning) | AI clones a person’s voice using short samples to make them say things they never said. | In 2024, a cloned voice of the LastPass CEO was used on WhatsApp to scam an employee, part of a 680% surge in voice deepfake attacks. | Source |
| Images | Single-frame fake images used to spread misinformation or manipulate markets. | In 2023, a fake Pentagon explosion photo went viral, briefly causing the S&P 500 to drop. | Source |
| Text | AI-written fake news, propaganda, or reports meant to deceive or manipulate. | False political posts and fabricated financial analyses created with AI tools have spread online. |
Voice cloning is the most dangerous among all formats, because it’s accessible and easy to create.
Video deepfake technology is threatning too, but they still need powerful computers and long processing times.
A fake voice can be created in just a few minutes, sometimes using nothing more than a 60-second audio clip.
These cloned voices are already being used in phone scams, fake executive calls, and call-center fraud.
But it doesn’t stop there. Deepfake technology is evolving fast, and two new formats are already causing trouble.
- Digital Document Forgery
AI can now create or alter official documents such as passports, ID cards, even financial statements. In 2024 alone, cases of digital document forgery shot up by 244%, making up more than half of all document fraud worldwide. Many of these attacks are targeting national ID systems like India’s Tax ID and Pakistan’s National Identity Card.
- Biometric Spoofing (KYC Bypass)
Then there’s biometric spoofing. Deepfakes made to trick facial or voice verification systems. Think of the identity checks used during bank sign-ups or corporate onboarding. Attackers now use synthetic faces or voices to bypass these systems, and such attacks jumped 704% in 2023. That’s why simple “liveness checks” is no longer enough.
The Rise of Deepfake Technology
Let’s zoom into the data.
| Metric | 2023 | Projected 2025–27 | Key Insight |
| Deepfake files in circulation | 500,000 | 8 million | Explosive 900% growth |
| Deepfake-related fraud attempts | Baseline | +3,000% YoY (2023) | Organized, large-scale exploitation |
| Average business loss per incident | — | ~$500,000 | Serious financial risk |
| AI-driven fraud losses (U.S.) | $12.3B | $40B (by 2027) | 32% yearly increase |
| Human detection accuracy | — | 24.5% | Manual review no longer reliable |
To fight deepfakes, we need technology that learns as fast as the fakes do. And one of the most reliable Deepfake detection tools nowadays is TruthScan.
If you don’t know about this, it is a real-time deepfake detection platform built for scale. It uses Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to spot the smallest inconsistencies across video, audio, and text.
Several tests have shown that TruthScan reaches up to 98% accuracy, compared to roughly 70% with older forensic tools.
It runs continuous checks across digital channels. It means organizations can detect deepfakes before they cause damage, not after.
From Entertainment and Memes to Serious Threats
Deepfake technology began as entertainment. As we’ve mentioned above, reddit users were swapping faces for laughs, creating memes, and enhancing movie scenes.
Hollywood even used it for digital de-aging and post-production magic. But that lighthearted phase didn’t last long.
In 2017, the first major misuse appeared. It was a non-consensual deepfake pornography.
From 2018 to 2022, Deepfake technology moved from harmless fun to a serious tool for manipulation and crime.
Early examples include the deepfake video of Gabon’s president in 2018, which triggered political unrest. By 2023, with powerful tools like Midjourney 5.1 and DALL·E 2, deepfake creation became effortless, and dangerous.
Then the time came when it’s no longer just public figures being targeted. Everyday people now face deepfakes used in harassment, blackmail, and revenge.
Fake videos have even surfaced in divorce cases, job applications, and internal corporate disputes.
Cases of Political and Corporate Misuse
Deepfake technology has officially entered business and politics side.
Examples of Corporate Misuse:
In 2024, scammers tricked employees at Arup using deepfake video and voice cloning. They pretended to be top executives in a live video call and convinced staff to transfer $25.6 million. The scam worked because people trusted the familiar face and voice on screen.
That same year, hackers targeted LastPass by cloning the CEO’s voice on WhatsApp. They used it to pressure an employee into taking urgent action after hours. These kinds of scams are becoming common because criminals can easily find public recordings, like interviews or speeches to copy someone’s voice or face. This means any executive who appears online could become a target.
Examples of Political Misuse:
The World Economic Forum named AI-driven disinformation one of the top global risks of 2024, with deepfakes at the center of it.
In August 2024, researchers uncovered the Spamouflage Network, a social media operation believed to be linked to China, which used deepfakes to discredit the President of the Philippines.
Similar tactics have been seen in warfare, like fake videos of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy appearing to surrender.
Risks and Dangers of Deepfakes
Let’s break down how deepfake technology is changing the very idea of what we can trust.
- Risks to Governance and Trust
If everything can be faked, what can we trust? Deepfake technology has shaken our confidence in digital information. Whether it’s a politician’s speech, a breaking news clip, or a viral video, most people now wonder, “Is this real or AI-generated?”
This growing doubt makes it harder for governments, journalists, and institutions to maintain credibility. As we saw earlier, deepfakes have already been used to spread political misinformation and even mimic public officials.
- Financial and Corporate Catastrophe
In the financial world, deepfake technology is fast becoming a billion-dollar problem. Scammers are now using cloned voices, fake videos, and synthetic identities to trick employees, investors, and entire corporations.
We’ve seen how executive impersonations and market manipulation incidents can shake major companies, all it takes is a convincing video call or a familiar voice saying the wrong thing.
- Technical and Social Vulnerabilities
Deepfake technology is breaking systems we once thought were foolproof. Facial recognition and voice verification which were once trusted for security, can now be bypassed with AI-generated faces and voices.
This means even “evidence” like a photo or video can’t automatically be trusted.
On top of that, human behavior adds to the risk. Older people and heavy social media users are more likely to believe and share deepfakes, helping them spread even faster.
How TruthScan Protects Organizations
TruthScan is a deepfake detection tool which adds a verification layer for reality itself.
How is this different from traditional systems?
Traditional deepfake detection systems only analyze visuals or audio, but TruthScan uses multi-modal verification.
What is multi-modal verification?
It means it cross-checks video, audio, text, and metadata in real time to spot inconsistencies that human eyes and legacy systems miss.
- It validates source authenticity before content is published or shared. It ensures brands, executives, and institutions don’t unknowingly amplify manipulated media.
- It fortifies identity verification against voice cloning and face-swap attempts by detecting synthetic fingerprints invisible to the naked eye.
- It protects organizational trust by preserving content provenance, so every verified video or document carries an unbroken chain of authenticity.
In a world where truth itself is under attack, TruthScan deepfake detection tool detects the fake, and restores confidence in what’s real.
How to Detect Deepfakes: Best Methods for Spotting Fake Media
Detecting deepfake technology requires a three-layered defense such as human review, forensic analysis, and adaptive AI detection.
-
Manual Ways to Detect Deepfakes
A trained reviewers can correctly identify high-quality deepfakes only 24.5% of the time. There are traditional telltale signs like mismatched lighting, unnatural shadows, or off-sync lip movements which have become unreliable.
Modern GANs smooth out those flaws, and once the video is compressed (like on social media), those minor cues completely disappear.
-
Technical and Analytical Approaches
This method is more reliable than manual review, but it comes at a heavy computational cost.
Let’s understand how these approaches work:
It starts with forensic analysis techniques which is the foundation of technical deepfake detection. These tools break media into microscopic details to see inconsistencies invisible to humans.
For instance:
- Frame-by-frame analysis dissects videos into individual images, which helps identify unnatural patterns like irregular lighting or mismatched facial movements.
Then comes Error Level Analysis (ELA), which reverses the editing process by highlighting differences in pixel compression. It is a telltale sign of manipulation.
As we move deeper, spatio-temporal coherence methods analyze how voice, gestures, and facial expressions align over time. Even a minor delay between lip movement and audio can betray a synthetic origin.
But while these methods are powerful, they’re also resource-hungry. Processing thousands of videos frame by frame isn’t practical at scale, especially when millions of new media files are uploaded daily.
Deepfake technology evolve because of how this is made. Each time a deepfake detector improves, the fake generator (the “adversary”) learns from it and produces even more convincing results.
This constant back-and-forth is known as adversarial loop. It means that static deepfake detection systems become outdated within months.
The only sustainable defense is AI that learns in real time, using neural networks to constantly update itself as new deepfake techniques emerge.
-
Using TruthScan AI Detection Tools
All of the methods we have seen above are still not that advanced to accurately detect deepfake technology. The speed, scale, and sophistication of these attacks demand specialized, adaptive AI systems built specifically for this evolving battlefield.
That’s where TruthScan comes in. TruthScan is specifically designed for real-world defense.
- Its AI-powered learning system never stops training, it studies new types of deepfake technology daily and updates itself automatically. This means it can spot even the most advanced “zero-day” deepfakes, the ones no one’s seen before, without needing humans to retrain it.
- It also works in real time across all major communication channels from video calls and call centers to digital media platforms. TruthScan doesn’t just analyze one thing. It checks video, audio, and text together, making sure everything lines up.
Here’s how it protects different types of organizations:
- Financial Institutions: TruthScan catches fake voices in customer support calls, blocks deepfake technology identities during KYC checks (which are rising fast), and prevents fake executives from approving fraudulent wire transfers.
- Enterprises: It keeps internal communication real. It flags tampered media that could be used for blackmail, misinformation, or brand damage. It can also analyze older communication records to detect patterns of synthetic content, building long-term security.
- Government and Public Sector: TruthScan verifies media used in investigations and public announcements, protecting against fake political videos or manipulated statements that could disrupt public trust or national security.
TruthScan is a deepfake detection tool that gives organizations the speed, accuracy, and adaptability needed to stay ahead.
Conclusion
Deepfake technology started as a clever experiment. It was a way to put Nicolas Cage’s face on everything.
But now, it’s crashing board meetings, election campaigns, and bank accounts. And the joke’s over.
What was once “harmless fun” on Reddit has turned into a billion-dollar fraud machine.
The scary part?
Most people still can’t tell what’s real. Even experts only spot high-quality fakes about a quarter of the time. The line between seeing and believing has officially blurred.
And the deepfake detection tools we once trusted to catch manipulation are already a step behind.
The fakes keep learning, adapting, and improving.
That’s why the future of digital defense depends on AI that fights AI.
Deepfake detection tool like TruthScan has adaptive systems that evolve in real time and detects what humans can’t.
In a world where anyone can “say” or “appear” to do anything, truth isn’t dead, it just needs better security.
Because the next viral video might not just be fake news… it might be a fake you.