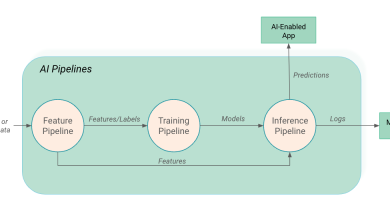
As artificial intelligence continues to grow in sophistication, today’s leaders are taking steps to strike the right balance between innovation and security.
This is because at a time when governments and businesses are eager to unlock the prospects of AI, many are also prioritizing data privacy. While AI models rely on data to spot patterns and make predictions, leaders understand that the private data used to train these models could potentially be misused. This poses a risk to their organization’s intellectual property, customer information, and other sensitive data.
To help manage the risks, many have turned to private AI, an approach that uses AI systems in a way that protects data privacy and maintains an organization’s control over sensitive data.
It’s important to keep in mind that public and private AI can complement each other depending on the specific use case. For example, while public AI is commonly used in many industries due to its scalability, accessibility, and other factors, private AI is critical in sectors like aerospace and defense or healthcare, where AI often handles sensitive data with national or global security implications.
Based on our experience in helping customers across different industries unlock AI’s potential while protecting privacy and mitigating risk, here are five key benefits of private AI:
- Addresses regulatory compliance
At a time when securing and protecting the privacy of consumers is top of mind for governments and businesses, one of the reasons organizations are adopting private AI is to comply with rules and regulations over data privacy.This is particularly the case in sectors that are more regulated than others, such as the aerospace industry, which often intersects with the military, intelligence agencies, or government contractors.
For instance, DXC partnered with the European Space Agency to develop a scalable AI platform aimed at increasing efficiency within its shared services organization. Called “ASK ESA,” the platform enabled the intergovernmental agency to quickly and efficiently access large volumes of data and documents and deploy AI applications across a range of departments. For the Agency, using Mistral AI (a European large language model hosted in its data center) gave officials the confidence that data remained safe within ESA under strict compliance and security rules.
- Maintains control over sensitive and proprietary data
Private AI is designed to provide organizations with more control over how enterprise data is used and accessed. Instead of sending internal data into public AI models, organizations can maintain control over confidential information by installing guardrails, where needed, across AI systems and workflows.
This is the approach Portugal’s largest telecommunications services provider took when leaders at MEO sought to find a simpler process for complying with regulators through the development of an AI assistant.
Because MEO operates within the telecommunications industry, which is often required to address evolving regulations due to the sector’s impacts on infrastructure, competition, and consumer protection, the company’s legal team spent ample time and resources manually cross-referencing large volumes of confidential corporate legal records to respond to new regulatory requests.
MEO wanted to find a more efficient way to respond to regulators. In collaboration with DXC, MEO developed an AI assistant that streamlined the extraction and standardization of regulatory response information from legal documents.
- Deepens trust with customers and key stakeholders
Demonstrating a commitment to data privacy and security can deepen trust with customers. This is particularly important for industriesthat routinely handle sensitive information, such as the infrastructure sector, where the construction, service, and maintenance of things like highways, bridges, and airports often involve assets critical to a city, state, or country’s essential services and public safety.
For example, when Ferrovial aimed to streamline its business operations, the Spanish infrastructure company headquartered in the Netherlands sought the help of DXC’s AI Workbench—a generative AI platform that deployed more than 30 AI agents to enhance efficiencies and safety measures across the organization’s workflows.
Because of the sensitive nature of Ferrovial’s work helping organizations and governments service critical infrastructure, the company needed to integrate secure and responsible AI technologies.
DXC’s AI Workbench was able to address Ferrovial’s need for privacy controls, helping the company improve operations for its 24,000 employees.
- Strengthens competitive advantage
AI systems that are built and deployed privately within an organization (versus using public or shared models) can give companies a competitive advantage—enabling them to use their own data in a smarter, faster, and more secure way.
This is especially true for many industries that often handle proposals from prospective clients. A good example is Ventia, an infrastructure services provider serving Australia and New Zealand. The company needed help with the time- and resource-intensive process of responding to bids, which involved spending days manually retrieving internal documents from previous bids.
Ventia partnered with DXC’s data and AI team as well as its cloud (AWS) practice to develop “Tendia,” an advanced GenAI solution that’s trained on Ventia’s record of historical tender submissions.
Tendia, which uses a RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) framework that helps fetch relevant data from relevant sources at inference time, allows Ventia to prepare responses to bids more quickly and efficiently without compromising the privacy of the data collected.
For example, instead of manually searching through SharePoint folders for bid-related information, Ventia’s bid support team can ask the generative AI assistant questions and receive answers within seconds, saving them time to focus on developing more compelling and competitive bids for clients.
- Minimizes errors and improves accuracy and quality
In some cases, the main goal of private AI isn’t to protect sensitive data but to unlock and organize a government’s vast collection of public data—making accurate and reliable information broadly accessible.
A good example is Italy’s Ministry of Culture. To make it quicker and simpler for researchers, museums, educators, and others to access cultural heritage documents through a single portal linked to Italy’s more than 6,500 libraries, the ministry partnered with DXC to develop an AI agent.
Using a technology called a GraphRag along with a well-organized knowledge system, the portal can structure information about cultural objects, historical events, and how they’re connected in a format that allows the AI agent to respond to users’ queries with accurate and trustworthy answers linked to credible sources.
Because the AI agent can run in a secure, government-controlled environment instead of a public cloud service, the ministry maintains data sovereignty and can keep national cultural data in Italy.
At a time when both governments and businesses are eager to harness AI’s potential, the growing emphasis on data privacy has led many to turn to private AI and to partner with the right enterprise AI solution provider. This approach to using intelligent AI systems while safeguarding sensitive information offers a powerful path forward for organizations.