- Clinically and statistically significant superiority of AP301 maintenance dose versus ineffective low dose in reducing serum phosphate levels was established and AP301’s efficacy is sustained throughout the 52 weeks of treatment.
- The non-inferiority of AP301 to sevelamer carbonate in reducing serum phosphate levels was demonstrated.
- Overall, AP301 was safe and well-tolerated. The most common AEs were discolored feces and diarrhea. Diarrhea generally occurred early and resolved without treatment changes.
- No evidence of iron accumulation was observed with cumulative AP301 exposure.
SHANGHAI, Nov. 7, 2025 /PRNewswire/ — Alebund Pharmaceuticals (“Alebund” or the “Company”), an integrated biopharmaceutical company focusing on developing innovative therapies for the treatment of renal diseases and related chronic conditions, presented the pivotal phase 3 study results of AP301 in patients on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis with hyperphosphatemia (RESPOND-1 study, NCT07030595) at the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) 2025 Congress in Houston, Texas.
AP301 is a novel fiber-iron-based phosphate binder that offers high phosphate-binding capability, does not require chewing before swallowing, does not expand in volume when exposed to gastric fluid, and is not systemically absorbed. These features contribute to a reduced pill burden, improved tolerability, and enhanced patient adherence.
The RESPOND-1 study was a randomized, open-label, active-controlled, multi-center study designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of AP301 in controlling serum phosphate levels in dialysis patients with hyperphosphatemia. The 52-week study included an active control phase, an AP301 low-dose control phase, and an extended treatment phase. Sevelamer carbonate served as the active comparator throughout the entire study period. The study was conducted at 50 investigational sites in China, and was led by Professor Li ZUO, Director of the Department of Nephrology at Peking University People’s Hospital.
In this study:
- Of 692 participants screened, 474 participants were randomized (3:1) to the AP301 or sevelamer carbonate arm; 187 eligible participants in AP301 arm were further re-randomized (1:1) at Week 24 to the AP301 maintenance dose (N=94) or low dose (N=93) arm. Overall, 396 (84%) participants completed the study.
- The primary efficacy endpoints included: 1) the change in serum phosphate levels during the low dose control phase from Week 24 to Week 27 between the AP301 maintenance dose and low dose arm in responders defined as serum phosphate level <1.78 mmol/L (5.5 mg/dL) by Week 20; 2) the change in serum phosphate levels from baseline to Week 12 between AP301 and sevelamer carbonate during active control phase.
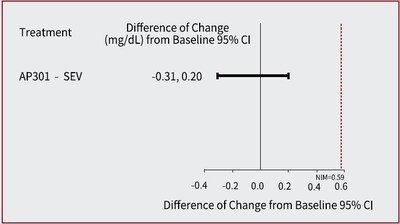
- At week 12, AP301 demonstrated non-inferiority to sevelamer carbonate, with a least squares mean (LSM) difference of -0.02 mmol/L(95% confidence interval (CI): -0.10, 0.06)[-0.06 mg/dL (95% CI: -0.31, 0.20)]; the upper CI bound of 0.06 mmol/L (0.20 mg/dL) was below the pre-defined non-inferiority margin (NIM) of 0.19 mmol/L (0.59 mg/dL). (see Figure 1)
- At week 27, AP301 maintenance dose showed a clinically and statistically significant superiority on serum phosphate control over an ineffective AP301 low dose in the low dose control phase {LSM difference -0.58 mmol/L (95% CI: -0.69, -0.47; P <0.001) [-1.8 mg/dL (95% CI: –2.1, –1.5; P <0.001)]}. (see Figure 2)
- AP301 achieved robust and sustained serum phosphate reduction over 52 weeks, suggesting its long-term therapeutic benefit (See Figure 3). It also showed a numerically higher serum phosphate response rate in the AP301 arm (66.7%) compared to the sevelamer carbonate arm (58.6%) at Week 52, and with a lower mean daily dose exposure (6.52 g/day in AP301 versus 7.56 g/day in sevelamer carbonate).
- Most participants experienced at least one AE (96.3% in AP301 and 90.8% in sevelamer carbonate). Diarrhea was the most common AE leading to study discontinuation in the AP301 arm (2/355, 0.6%), typically occurring within the first 2–4 weeks and predominantly mild in severity.
- Iron parameters changed from baseline mainly during the first 24 weeks, then stabilized or decelerated thereafter. No evidence of iron accumulation was observed with cumulative AP301 exposure.
Presentation Details at The American Society of Nephrology (ASN) 2025 Congress
Date: November 6, 2025
Title: 52-Week Phase 3 Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of a Novel Iron-Based Phosphate Binder AP301 in Patients on Dialysis with Hyperphosphatemia
“Iron-based phosphate binders have been used with increasing frequency in recent years for certain advantages. As a new generation of iron-based phosphate binder, AP301 is well differentiated from other iron-based phosphate binders with no systemic absorption and no need to chew or crush before swallowing. This pivotal trial demonstrates the clinical value of AP301 and its potential to advance the treatment option for patients with hyperphosphatemia.” Dr. Jin Tian, Co-founder and Chief Medical Officer of Alebund, commented, “Alebund is actively engaging in discussions with the China National Medical Products Administration regarding the new drug application plan for AP301.”
About Hyperphosphatemia
Hyperphosphatemia is one of the most common complications in CKD patients. The long-term elevated serum phosphate levels could cause multiple complications such as secondary hyperparathyroidism, renal osteodystrophy, and vascular calcification. It is an independent risk factor of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortalities. Good control of serum phosphate levels could effectively improve the patients’ outcome. For CKD patients undergoing dialysis treatment, regular dialysis is not sufficient to remove the excess serum phosphate in the body. Considering the limitations of low-phosphate diet which might cause dystrophia, oral use of phosphate binders is the prevailing treatment for hyperphosphatemia. However, existing phosphate binders lead to low patient compliance, with less than 50% of patients achieving good phosphate control, due to gastrointestinal side effects and high pill burden, etc.
According to the Global and Chinese Hyperphosphatemia Drug Industry Blue Book by China Insights Consultancy in 2023, the out-of-target rate of serum phosphate level in dialysis patients in Chinese mainland was significantly higher than that in other countries and regions. There remains substantial room for improvement in terms of the proportion of patients using phosphate binders and duration of their usage. The market size of serum phosphorus-lowering products in China is expected to reach RMB10 billion by 2035.
About Alebund Pharmaceuticals
Alebund was founded in Shanghai in 2018. The Company focuses on the discovery, development, manufacturing, and commercialization of novel therapies primarily for kidney diseases and their complications, as well as other chronic conditions, to bring better therapeutic options to patients in China and globally. Alebund has built a diversified and balanced pipeline of seven drug candidates and one commercialized product (Mircera®) targeting a broad range of renal indications, including chronic kidney disease (CKD) and CKD complications, such as hyperphosphatemia, renal anemia, IgA nephropathy, diabetic kidney disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), and autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Alebund has completed the construction of its manufacturing site in Yangzhou that will supply both drug substance and drug products of our product candidates, including AP301, upon commercial launch. Alebund has also established a dedicated in-house commercialization team in China responsible for promoting our renal products.
View original content to download multimedia:https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/alebund-presents-phase-3-trial-results-of-ap301-at-the-american-society-of-nephrology-asn-2025-congress-302605683.html
SOURCE Alebund Pharmaceuticals






