A few years back, automation meant bots that followed scripts. They clicked, typed, copied, and pasted exactly as told. But throw in an exception like a new format of document or a moderately complex customer request, those bots stopped working. Human intervention was a must.
That is no longer the case.
We are now seeing AI agents that don’t just follow instructions; they make decisions, learn from outcomes, and adapt in real time. This shift is what Agentic AI is all about.
While there is no shortage of AI trends being discussed almost at every platform, this piece focusses on the ones that are not just trends anymore but have also been showing results with practical implementations in real-time business operations.
Instead of building on the content around an exhaustive list, we have filtered our observations and insights into six AI and automation shifts that have defined the first half 2025 and are turning into a central pillar of enterprise strategy for the times ahead.
Let’s begin with the talk of the town. Agentic Automation and the impact of autonomous systems on businesses.
#1. The Rise of Agentic AI
With more and more complex, unstructured data mounting in, organizations are always under pressure to move things faster than ever. Though things could be done with automation, simple automation is not just enough anymore.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) still plays a vital role in handling routine tasks, but it needs more support. Agentic systems are built for use cases where the response is not obvious and where both context and flexibility are important. This is where an intelligent and more responsive ecosystem comes to play involving AI agents, bots, and human teams.
Let’s explore three core areas of function where agentic systems empower teams.
1. Business Operations
Instead of employees manually checking emails or exceptions, an AI agent can read, understand, and act without any rule-based fixed system. These agents are tailored according to individual tasks and can help in tasks like claims processing, onboarding, candidate screening, patient data management, and more by reducing escalations and reacting to real-time changes.
2. Developer Workflows
Developers can guide and leverage AI agents using plain language or low-code tools. The agents run processes, handle errors, and explain failures, making the software development cycle including testing easier and more outcome focused.
3. Customer Experience
AI agents provide fast, relevant, and human-like responses. They adapt to the customer’s issue, take appropriate action, or escalate with context, leading to quicker, more personalized support.
What You Get by Deploying Agentic AI?
Deploying Agentic AI offers clear benefits when done right. One of the best-known advantages is that it instantly improves productivity by combining agents, bots, and humans to reduce turnaround time. With 24/7 availability and fewer manual steps, it ensures consistent, accurate outcomes. By automating both complex and routine tasks, agentic systems help cut costs and reduce rework. Also, their modular, self-learning nature makes it easy to scale tailored to business requirements. The best part is that they deliver faster, more customer experiences that improve satisfaction without involving too many people for the same task.
Common Agentic AI Challenges and How to Attend Them
As promising as the agentic systems might be, it still requires careful implementation. But the best part is these are potential challenges that can be easily managed with the right insights and strategy. Here we go.
- Assign clear, non-overlapping tasks to agents
- Monitor them to ensure performance and decision accuracy.
- Define goals upfront to avoid misaligned actions.
- Ensure data used is reliable and secure.
- Stay compliant with privacy laws.
- Plan for integration challenges, especially with older systems.
#2. Generative AI: Moving Beyond Text with AI Agents
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence model built on large language models (LLMs) that can generate things like text, images, audio, video, and even codes. These systems use a lot of data to learn and then make outputs that are similar to how humans operate. In its initial stages, this technology was only used to write blog posts, answer questions, or summarize documents. But now, it is growing and has evolved with gen AI agents.
Generative AI agents are self-sufficient, smart digital workers that use generative AI to think, do things, make choices, and act on their own in real time. They don’t need much human supervision and can change how they work based on any new information or feedback. This makes them more proactive coworkers than just a tool.
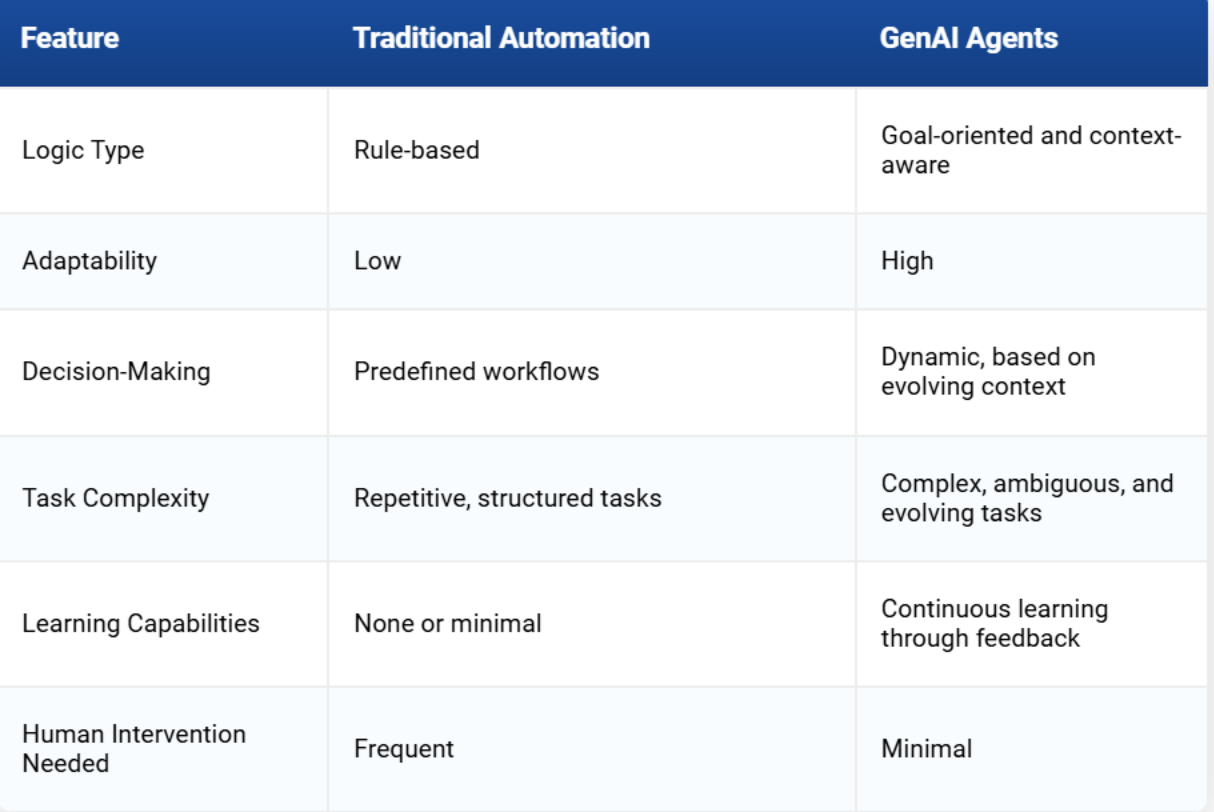
Difference between GenAI agents and traditional automation
How Enterprises Are Creating Impact with Gen AI Agents?
Organizations across industries are using generative AI agents to reinvent how they carry out their day-to-day workflows. Let’s have a look into it:
AI Agents for Healthcare:
Healthcare GenAI agents take care of prior authorizations, summarize medical records, and check payer coverage in healthcare. This helps healthcare practitioners to save hours spent on manual healthcare tasks and thus lowers clinician burnout.
AI Agents for Marketing:
Today marketers rely on smart AI agents to automate repetitive email writing, basic research, classifying and segmenting target audience, summarizing details, and quick decision making.
AI Agents for Customer Service:
For customer service, AI agents work on behalf of staff to interact with customers, solve problems independently, follow up, and even escalate issues around complex queries to human staff.
AI Agents for Finance:
Finance AI agents can handle end-to-end financial operational items, including accounts payables and receivables automation, mortgage automation, cash flow management, detecting potential frauds and maintaining regulatory compliance.
#3. Multimodal AI
Multimodal AI are artificial intelligence systems that can understand and process information from multiple formats like text, images, videos, and audio. It opens up completely new possibilities for creativity, automation, and user experience. Multimodal systems can understand and combine different types of data, which makes interactions more like those between people. This is different from traditional models that only work with one type of data.
AI can now describe a picture, make captions for a video, follow spoken instructions, and even make multimedia content from a simple prompt. The result is a user experience that is more immersive and aware of its surroundings, and that feels smart and intuitive.
AI-as-a-service platforms that offer multimodal content generation, training tools, and next-gen customer engagement are some of the new business models that actively make an impact across operations. In fact, it is the most dynamic way so far to connect human intent with machine understanding.
#4. AI in Workflow: What Is It and How It Works?
When asked about AI, the first response we can think of is how it has been automating routine jobs and optimizing productivity. But there is more to how AI is changing the way teams work now.
Beyond simple automation, enterprise AI agents have the capability to point out the root cause of a problem and assist in fixing the problem in a faster manner. They are integrated within enterprise systems and initiate multi-system processes, so teams can work on creativity and strategy.
How Does AI Enable Team Collaboration, Communication and Faster Decision-Making?
AI allows for breaking the isolation of tools and knowledge. It takes notes of meetings, manages action items, and follow-ups. While some AI assistants work like project co-pilots to sync the next steps, the others are the autonomous AI agents that open tickets, pull documentation, and alert teams without requiring manual entry.
AI transforms intuition into insight using real-time data, and modeling outcomes. For example, during the hiring process, it can pair resumes with the job requirements, mime notes sentiments, and suggest fit scores, exactly as in the case of AI-powered candidate screening, where agents assist in optimizing the recruitment. Agentic AI uses adaptive models that are goals oriented towards businesses.
Though AI agents streamline tasks, human-in-the-loop is still a necessary factor to ensure seamless end-to-end output. The best way to balance this out is by establishing an eco-system where AI does volume while humans add empathy and judgment for best results.
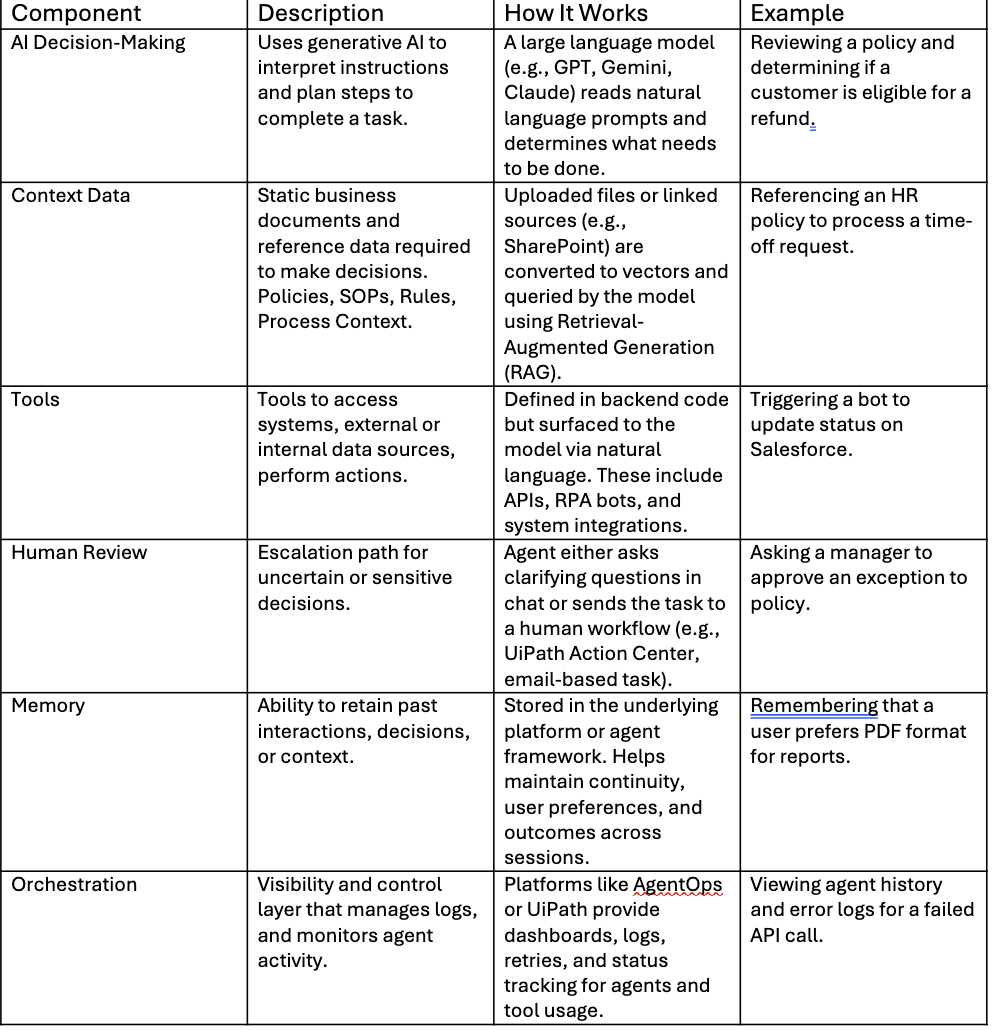
Anatomy of an AI Agent: Core Components & Governance
#5 Responsible, Ethical and Explainable AI: Why It Is More Important Than Ever
AI has become the primary element of business functionality. However, along with its abilities, there lies the threat of prejudice, false information, and malicious use, following which responsible, ethical, and explainable AI is needed.
AI has a consequence in real-life decisions, like generative models may hallucinate or encode prejudice. They can lose social approval and obedience without due control and governance. This is why Generative AI governance is needed to make sure it is used responsibly.
Trends Future & Ethical Practice
As LLMs and multimodal AI grow, governance, human direction, bias identification and explainability have become the new priorities of companies. Such tools as RAG and autonomous agent systems require a strong framework to be safe.
Regulations such as the EU AI Act, and increasing user awareness, are driving firms towards policies, audits, and opt-out options to protect ethical uses of AI.
Responsible AI establishes trust, talent attraction, risk mitigation, and compliance with the changing norms of behavior. Companies instilling explainability and fairness will receive compliance and a long-term reputation benefit.
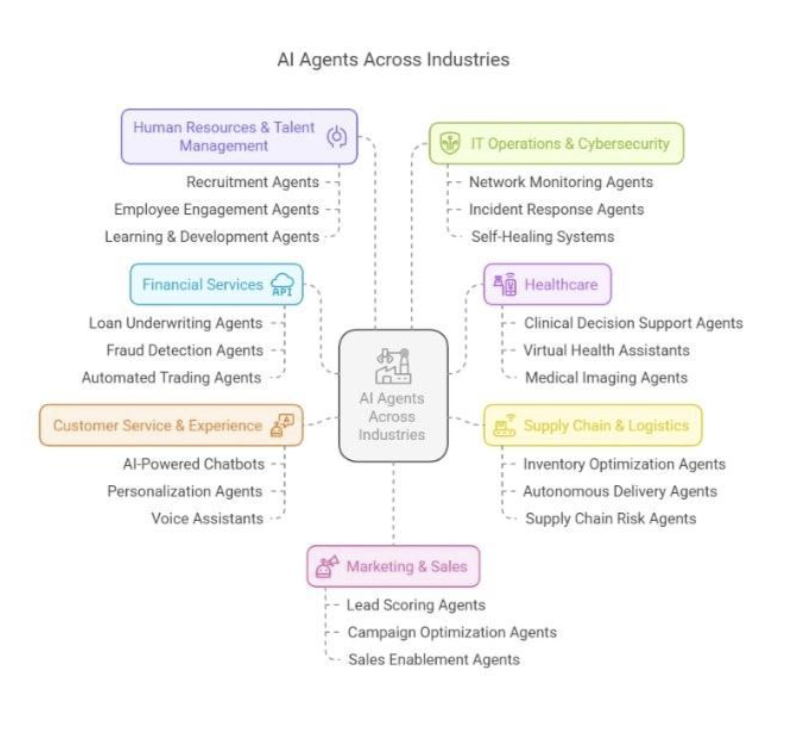
#6. AI Across Industries: Real Impact, Real Results
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a future concept; it is already reshaping industries with real-world impact. AI trends are evolving quickly, from detecting diseases early in healthcare to predicting equipment failure in factories and spotting fraud in finance. AI is helping businesses make better decisions, solve problems, and save time in every major industry. Here’s how AI is impacting healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
AI Agents across departments & industries
AI in Healthcare
AI is becoming a significant resource for medical providers, researchers, and healthcare administrators. It promotes faster, more accurate diagnoses, supports drug discovery, and makes complicated documentation easier. For example, Tempus uses AI to personalize cancer treatment by analyzing clinical and molecular data, PathAI, on the other hand, applies deep learning to make pathology diagnosis more accurate.
AI is making things less difficult for administrators in addition to helping with diagnostics. The AI Adoption in Healthcare Report 2024 says that top institutions are utilizing AI to automate clinical documentation. This cuts down on paperwork and speeds up patient flow. At Coherent Solutions, an AI-powered RX transcription tool was built to interpret optical prescriptions, reducing errors and helping patients receive tailored eyewear faster.
And while generative AI adoption in medicine is still maturing, the role of intelligent AI agents like virtual assistants that support patients with post-treatment care, are already showing how they can be a strong addition to human care.
AI in Finance
In financial services, AI is a powerful engine for both innovation and protection. Banks are using AI for real-time fraud detection, recognize patterns, and provide notifications when something unusual happens. Mobile banking apps now feature embedded AI that provides users with personalized budgeting advice, spending summaries, and even investment tips via automated advisors.
A McKinsey study estimates AI could deliver up to $1.2 trillion in additional GVA to the global financial industry by 2035. AI agents are being used internally to assist risk teams with compliance reviews, transaction monitoring, and faster resolution of flagged activities, minimizing manual workloads while improving audit readiness.
AI in Manufacturing
AI is helping manufacturers to improve product quality and keep them running longer. Predictive maintenance, which uses IoT sensors and machine learning, to discover mechanical faults before they cause failures, which saves time and money. Computer vision is used in visual inspection systems to find defects in real time on production lines.
A report from 2025 on the state of AI in manufacturing says that 77% of manufacturers have already implemented AI in some way, The most common uses are for inventory optimization, quality assurance, and production planning. Collaborative AI agents, or “co-pilots,” are increasingly being preferred over full automation, these agents help people make decisions instead of replacing them.
AI in Retail
Retailers are using AI to hyper-personalize customer experiences and keep operations smooth behind the scenes. Voice and visual search features, AI chatbots, and dynamic product recommendations are now common. But what’s happening behind the curtain is just as exciting.
A great example is how the strategic integration autonomous AI agents and MuleSoft cut down inventory delays by 90% and saved $3.8M per quarter in losses for a global retailer.
According to Deloitte’s 2025 Retail Outlook, merchants who used AI saw conversion rates go up by as much as 15% on Black Friday. This was because AI made it easier and faster to make decisions.
So Where Do We Go from Here?
Agentic AI is not science fiction anymore. It’s already in use and quietly powering processes in banking, healthcare, insurance, and beyond. What’s different is that these agents don’t just wait for instructions; they take action based on context learning.
It doesn’t mean we stop using bots or humans. Instead, we bring them together. This mix is already helping companies respond faster, make smarter choices, and serve people better.
The businesses that get ahead are the ones that recognize where agents fit, not everywhere, but in the right places. It’s not about replacing people. It’s about letting them focus on what matters while the system handles the rest. As we proceed with new trends and updates, keeping up and implementing them in time ensures maximum impact, minimal risk, and more scalable agents.