
Over the recent weeks, I’ve embarked on a deep dive into numerous surveys from 2023 and 2024, focusing on the real impact of Digital Transformation and AI implementation within enterprises. The insights unearthed may defy expectations, underscoring a pivotal truth: the mere possession of cutting-edge technology, regardless of its perceived capabilities, does not guarantee transformative outcomes for businesses. Success hinges on the readiness of the organizational ecosystem to embrace and effectively integrate these advancements.
Key Findings: A Closer Look at the Reality of Digital Transformation
A 2023 executive survey conducted by KPMG paints a telling picture: a staggering 51% of US businesses reported no noticeable improvement in performance or profitability from their digital transformation endeavors over the past two years. This revelation challenges the prevailing optimism surrounding digital advancement and calls for a critical evaluation of its practical benefits.
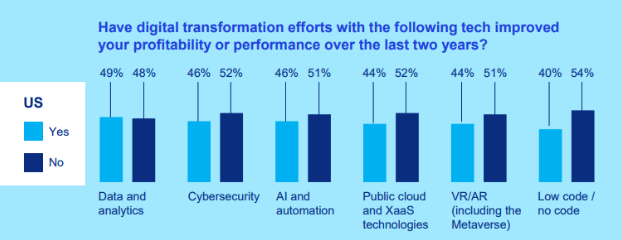
Further insight comes from PwC’s 2024 Digital Trends in Operations Survey, where a significant 69% of operations and supply chain officers reported that their technological investments failed to meet the anticipated outcomes, despite a notable 70% of companies having experimented with and adopted Generative AI. This discrepancy between expectation and realization underscores the complexity of achieving tangible results from digital innovation.
Turning the lens to AI, a study by MIT Sloan and BCG highlights that only a mere 10% of companies have reaped substantial financial benefits from their AI investments. IBM’s analysis deepens the concern, indicating that the average returns on AI are often less than the cost of capital, suggesting a disconnect between investment in AI and its financial viability. Complementing these findings, Eric Siebel’s research with Rexer Analytics reveals a sobering statistic: only 22% of data scientists report successful deployment of their new initiatives.
These insights collectively point to a crucial narrative: the journey of digital transformation and AI implementation is fraught with challenges, and the path to success is less about the technology itself and more about how it is strategically integrated and leveraged within the broader business ecosystem.
The Multifaceted Journey of Digital Transformation
The pursuit of Digital Transformation transcends mere technological acquisition; it’s a comprehensive journey that reshapes every facet of an organization. While the allure of technological potential is undeniable, it is the strategic orchestration of various elements that catalyzes long-term and substantial improvements. At its core, Digital Transformation is an intricate tapestry woven from several critical threads:
- Business Process Transformation challenges organizations to critically assess and revamp their existing processes, workflows, and systems, making them more efficient, effective, and adaptable to the digital era. This journey often involves embracing automation, digitization of workflows, and rigorous process reengineering.
- Business Model Transformation involves a radical rethinking of how businesses operate, leveraging digital technologies to shift from traditional models to innovative, often service-based or platform-driven models. This transformation may integrate digital products into existing portfolios or pivot the business direction entirely.
- Domain Transformation signifies the bold venture into uncharted territories or industries, empowered by digital capabilities. This expansion can lead to the creation of novel products, services, or business models that disrupt conventional market segments.
- Cultural/Organizational Transformation emphasizes the vital change within the organizational ethos, fostering an environment that champions innovation, agility, and a proactive digital-first mindset. It necessitates a shift in operational practices, leadership approaches, and the adoption of collaborative tools to enhance organizational flexibility and responsiveness.
- Customer Experience Transformation focuses on leveraging digital technologies to revolutionize how businesses engage with their customers, aiming for a seamless, personalized experience across all customer touchpoints. This strategic focus integrates AI, machine learning, and data analytics to better understand and anticipate customer needs.
- Digital Technology Integration encapsulates the strategic inclusion of advanced technologies like cloud computing, AI, IoT, and blockchain into the fabric of business operations. This not only involves adopting new technologies but also upgrading existing systems to enhance performance, scalability, and security.
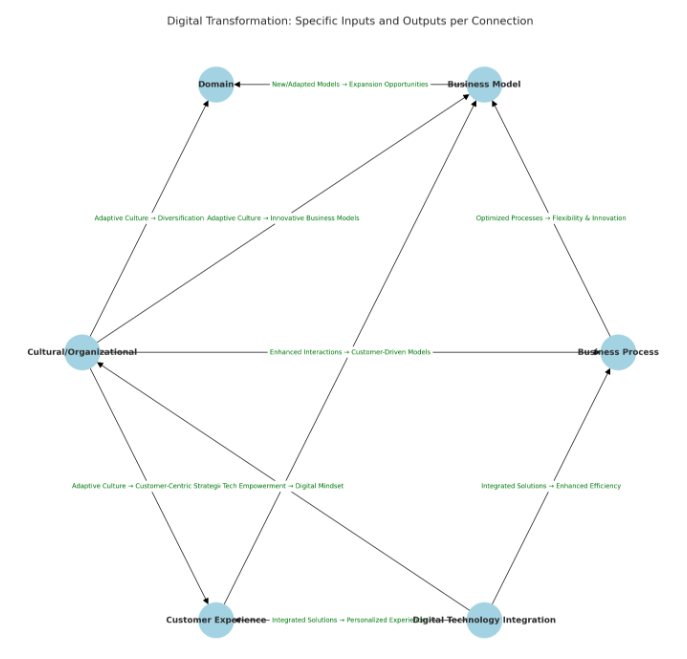
These components form a dynamic ecosystem, illustrating a profound interdependence and action-reaction synergy among them, as depicted in Figure 1 – a visualization of Digital Transformation Categories and their intricate relationships.
Challenge 1 – Complexity and Ambiguity of the Digital Technology Landscape
Numerous enterprises have embraced a wide array of digital solutions to modernize their operations. Among these, cloud computing (62%) and AI, notably machine learning (55%), have emerged as predominant choices, whereas ERP enhancements (27%) and data ecosystems (33%) have attracted lesser focus.
The process of fully integrating this diverse technological ecosystem presents significant challenges, particularly with AI Integration, which is still evolving in terms of maturity and expertise within many organizations.
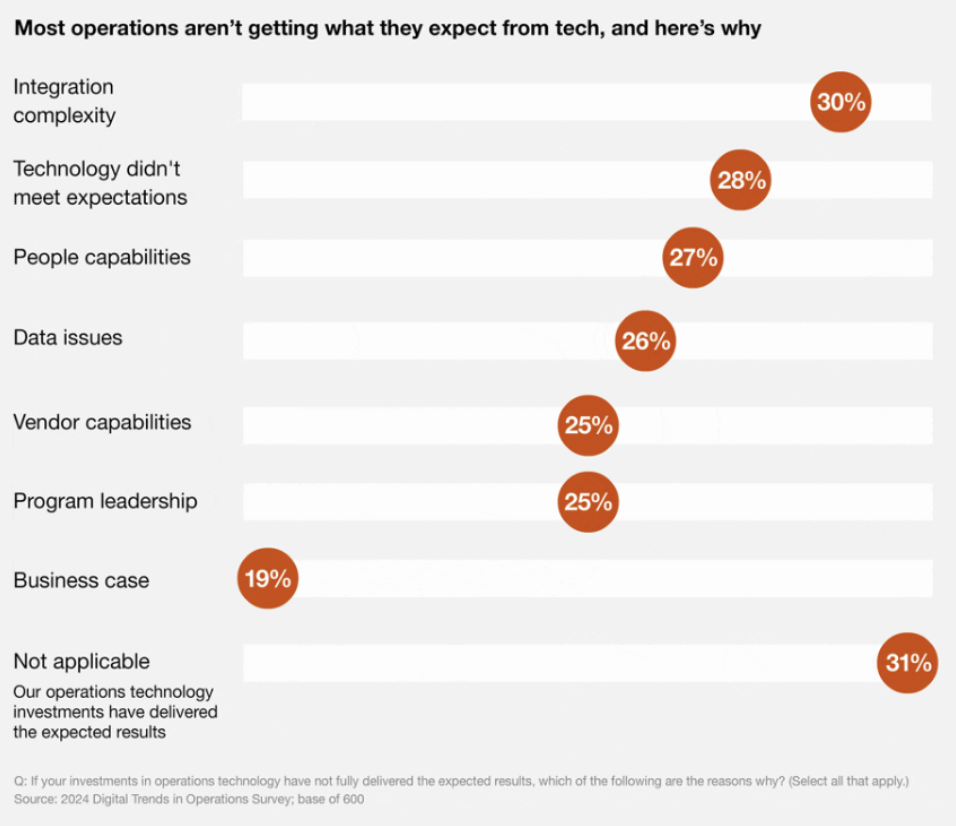
According to a PwC survey, 28% of respondents attributed their unsuccessful outcomes to technologies failing to meet expectations, a sentiment partially attributed to a general lack of expertise and, arguably, overzealous promises by technology providers. This underscores the necessity for businesses to deeply comprehend the capabilities and limitations of each technology, emphasizing the critical role of competence across all company levels.
Challenge 2 – The Undervalued Importance of Digital Skills
As depicted in “Figure 1”, “Tech Empowerment” through Digital Technology Integration plays a crucial role in cultivating a “Digital Mindset” within the Cultural/Organizational fabric, highlighting the importance of technology in spearheading cultural transformation. However, the involvement and empowerment of individuals in these transformative initiatives are often overlooked.
Many efforts I’m familiar with adopt a top-down approach, failing to adequately involve or empower employees in crafting solutions. The chronic issue of a digital skills gap remains a formidable barrier, with survey respondents frequently citing the scarcity of skilled digital talent as a primary obstacle to the digitalization of operations. This challenge emphasizes the significance of leveraging Cultural/Organizational dynamics to instill an “Adaptive Culture” conducive to achieving “Process Agility”.
Challenge 3 – The Need for Defined Objectives and a Forward-Looking Strategy
The absence of a coherent and consistent strategic framework often leads to shifting milestones and a propensity to prioritize short-term gains, overshadowing the broader vision. Bridging the gap between Technology and Business Stakeholders is essential for the articulation of clear objectives and the collaborative design of solutions that fully engage all parties involved.
Furthermore, a paradigm shift is needed concerning the primary objectives of digital initiatives; rather than focusing solely on cost reduction and the acceleration of decision-making processes, there should be a greater emphasis on innovation and the support of alternative business models. Leadership must play a proactive role in this context, advocating for an “Adaptive Culture” that empowers Cultural/Organizational forces to champion “Innovative Business Models” and foster “Diversification” within the realms of Business Model and Domain transformations.





